Computer Network (2)
건국대학교 컴퓨터네트워크 강의노트 2
Computer Networking: A Top down Approach
Chapter 3: Transport Layer (Cont'd)
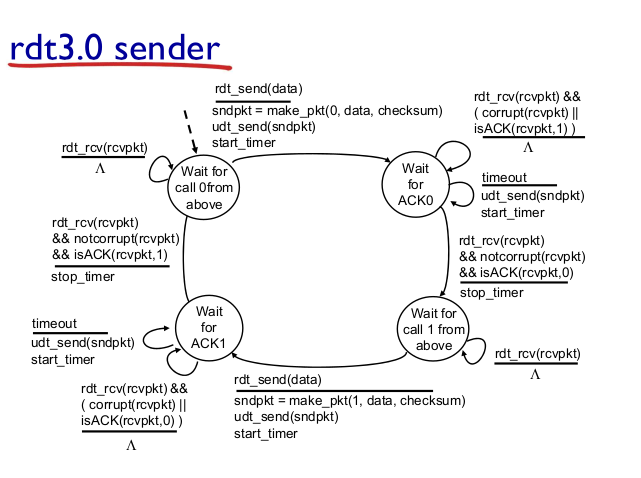
Finite State Machine (FSM)
- rdt 3.0: Timing
- sender가 ACK를 기다리는데, 어느정도 기다려도 오지 않으면 timeout
- reasonable timeout
- ACK가 그냥 delay 되는 거라면 retransmission은 중복. seq가 있어서 receiverㅏ 처리
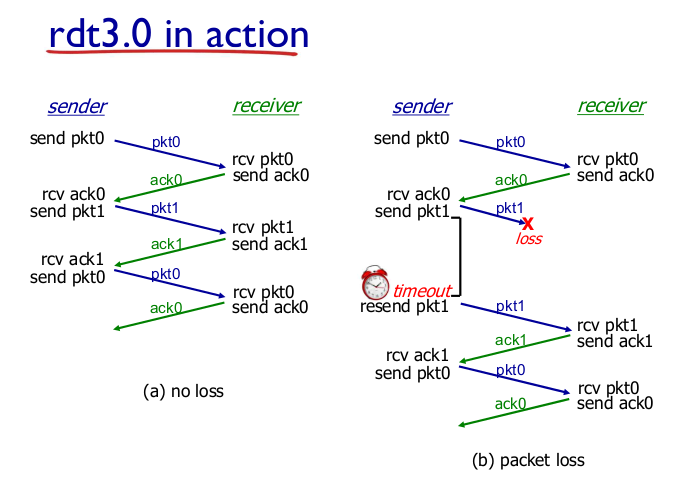
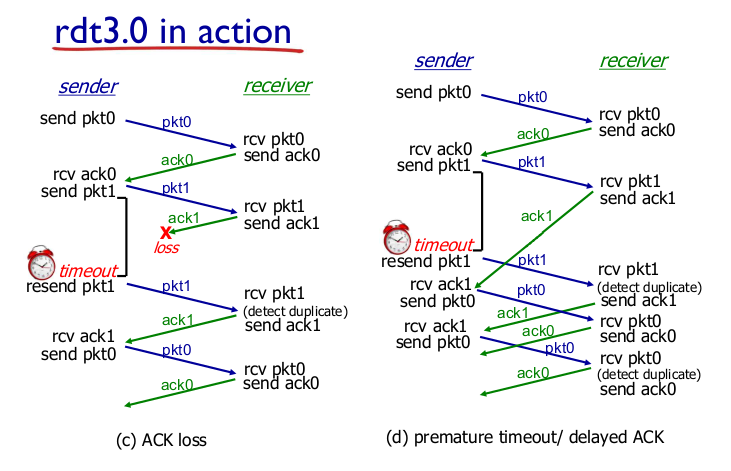
- Performance of rdt
- 동작은 좋은데 성능이 구리다
- ex) 1Gbpgs link, 15ms prop delay, 8000bit packet
$$ D(trans) = L / R = 8 microsecs $$
$$ U(sender) = (L / R) / (RTT + L / R) = 0.008 / 30.008 = 0.00027 $$
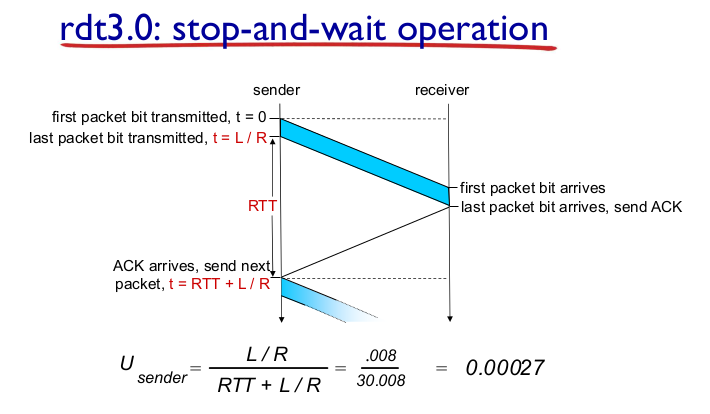
- 점유율이 0.00027. bandwidth 낭비. RTT동안 전송이 없으니까.
- rdt 3.0: Timing
Pipelined protocols.
병렬로 여러개 보낸다. buffer가 여러개 필요하다
- go-back-N
- Selective Repeat
Pipelining: increased utilization
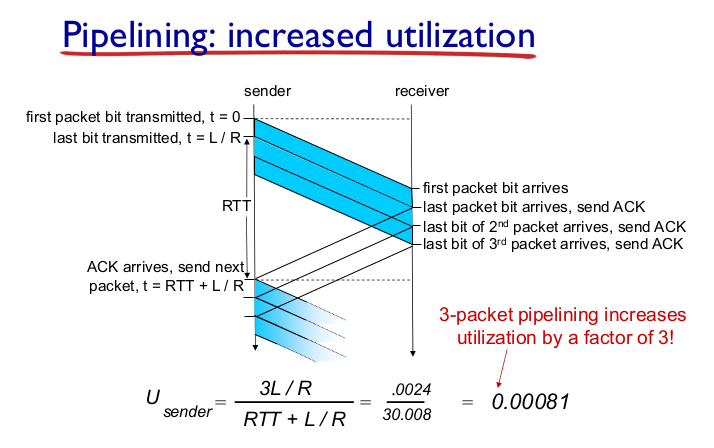 $$ U(sender) = (3L / R) / (RTT + L / R) = 0.024 / 30.008 = 0.00081 $$
$$ U(sender) = (3L / R) / (RTT + L / R) = 0.024 / 30.008 = 0.00081 $$- 3배 좋아짐.
Go-back-N
- n개: window size. [0 ~ n-1]
- ack없이 n개까지 보낸다.
- Cummulative ack
- 1, 2, 3, 4 있으면 4만 ack.
- 가장 처음 패킷 timer 측정 ack
Selective Repeat
- ack없이 n개까지 보낸다.
- Inidividual ack
- 1, 3 패킷마다 개별적 ack
- 매 패킷 timer 측정
Go-Back-N: sender
- sender도 reciever도 window 를 운영.
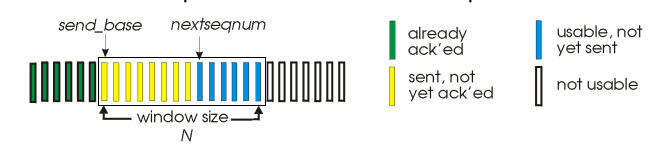
- Sliding window: ACK를 받을때 마다 window가 움직인다.
- duplicate ACK 가능성.
- 제일 오래된 패킷 기준 timeout. 다 다시 보낸다.
- sender extended FSM
- receiver extended FSM
- ACK-only: 가장 큰거
- out-of-order pkt:
- discard: no receiver buffering
- re-ACK: seq 가장 높은거.
- GBN in action
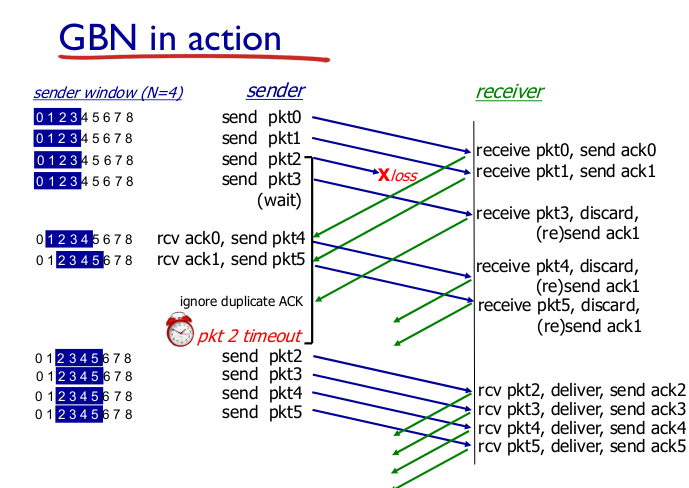
- 3, 4, 5 잘 갔는데 다시보낸다. 조금 비효율적.
- sender도 reciever도 window 를 운영.
Selective repeat
- GBN은 timeout시 다시보내는 패킷이 많다. (순서가 바뀌어오는거 다 버린다.)
- error난 packet만 재전송
- receiver: individually ack
- 매 패킷마다 timer
- window
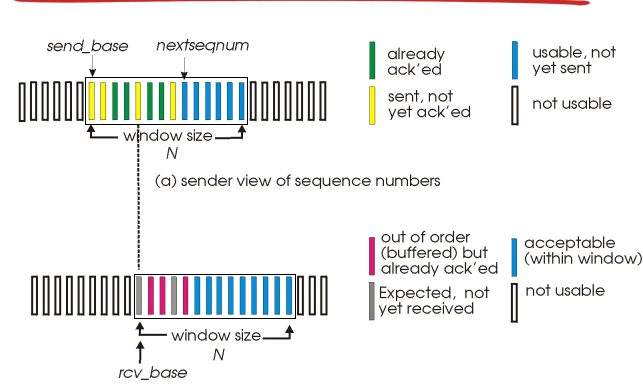
- sedner
- 데이터 available window, 패킷 전송
- timeout: 에러난 패킷만 재전송
- ACK
- 나머지는 놔둔다
- sedner
- Select repeat in action
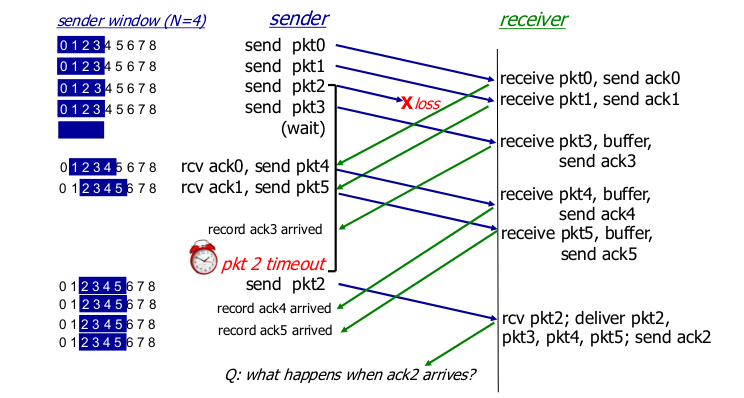
- 단점
- 패킷마다 timer
- buffer management
- 딜레마
- 윈도우 사이즈가 충분히 커야한다.
5. TCP
프로토콜이 제법 복잡하다.
Overview
- point-to-point: 1 sender - 1 receiver
- reliable, in-order-byte
- 시간이 좀 걸린다.
- bandwidth 보장 x
- pipelined (window size N)
- TCP congestion / flow control
- full duplex data
- 양방향 통신
- MSS: maximum segment size. 패킷 최대 길이 2^16
- Connection-ordiented
- handshaking 한다.
- flow controlled
TCP segment structure
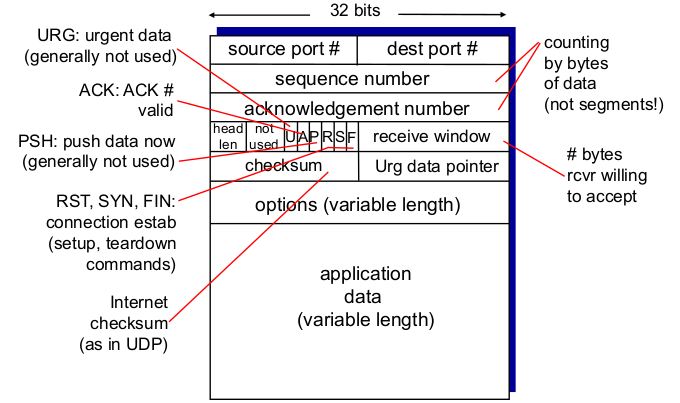
- 총 크기가 TCP는 20 bytes, UDP는 8 bytes. 옵션이 있으면 더 길다.
- sequence number: 0 ~ 2^31-1
- U: 급하다
- A: ACK only : P: Push. buffer가 차지 않았다.
- R: RST. 비정상종료
- S: SYN
- F: FIN
- receive window: window size N은 가변적.
- 매 윈도우 size는 0 ~ 2^16-1
- 3 -> 3만 넘치지 않게 보내라
- => flow/congestion control
- urg data pointer: urgent data 위치
TCP seg, numbers, ACKS
- Sequence numbers
- segment data의 첫번째 byte number
- 첫번째 패킷: 1, length 1024, MSS
- 두번째 패킷: 1025
- acknowledgements
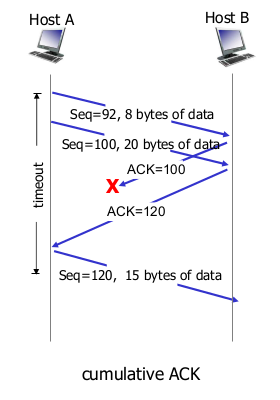
- cumulative ACK
- 첫번째 패킷 SEQ 1, MSS 1024 => ACK 1025
- 다음 SEQ 1025를 기대한다.
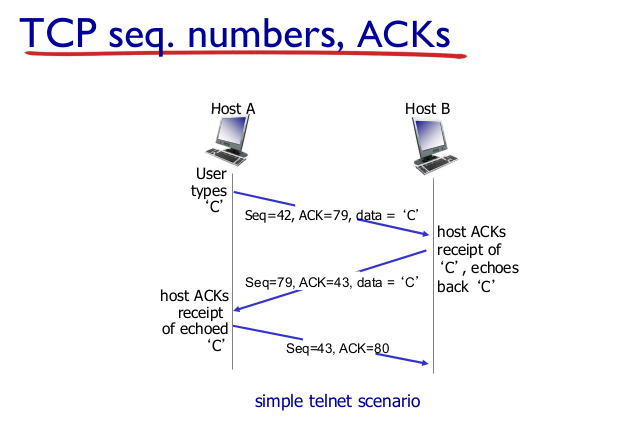
- cumulative ACK
- Sequence numbers
TCP round trip time, timeout
- timeout이 RTT보다는 커야지
- 그런데 RTT는 유동적
- too short: 불필요한 재전송
- too long: slow reaction
- RTT를 어떻게 재지?
- sampleRTT: 정상적인 패킷 RTT 계산. 최근 몇개 평균
$$ EstimatedRTT = (1 - a) * EstimatedRTT + a * SampleRTT $$s
- 보통 a = 0.125
- timeout interval: EstimatedRTT + “safety margin”
- EstimatedRTT 변동이 컸다면 -> safety margin도 크게 $$ DevRTT = (1-b) * DevRTT + b * (SampleRTT - EstimatedRTT) $$
- 보통 b = 0.25 $$ TimeoutInterval = EstimatedRTT + 4*DevRTT $$
- sampleRTT: 정상적인 패킷 RTT 계산. 최근 몇개 평균
$$ EstimatedRTT = (1 - a) * EstimatedRTT + a * SampleRTT $$s
- timeout이 RTT보다는 커야지
Reliable Data Transfer
RDT services
- pipelined segments
- culmulative acks
- signle transmission timer
retransmission triggered
- timeout events
- duplicate acks
TCP sender events
- app에서 데이터 전송하려 할 때
- segment를 seq로 만든다.
- seq -> byte-stream. 첫번째 byte의 byte number
- timer -> oldest unacked segment 기준
- expiration interval:
TimeoutInterval
- app에서 데이터 전송하려 할 때
timeout
- Retransmission
- Go-Back-N 이니까 oldest부터 다시 보낸다.
ack received
- window sliding
- timer restart
TCP sender
TCP retransmission scenarios
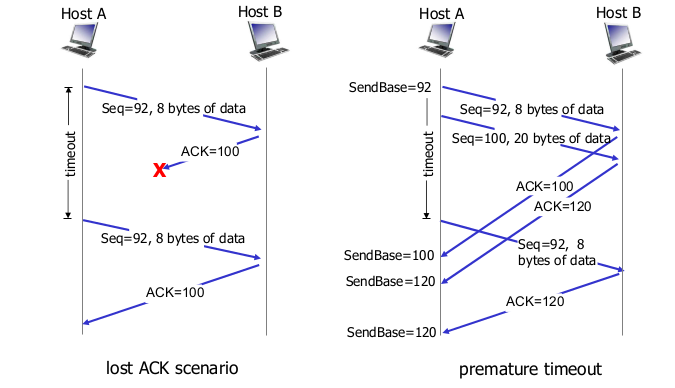
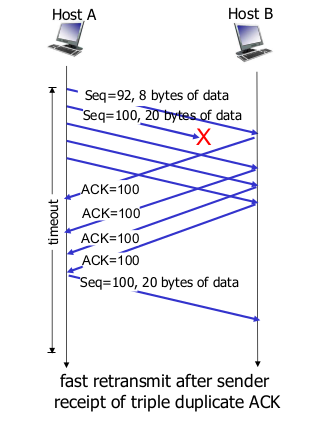
TCP fast transmit
- time-out period가 상대적으로 길다
- duplicate ACK가 쌓이면 transmit
- “triple duplicate ACK” => resend unacked segment with smallest seq #
TCP Flow control
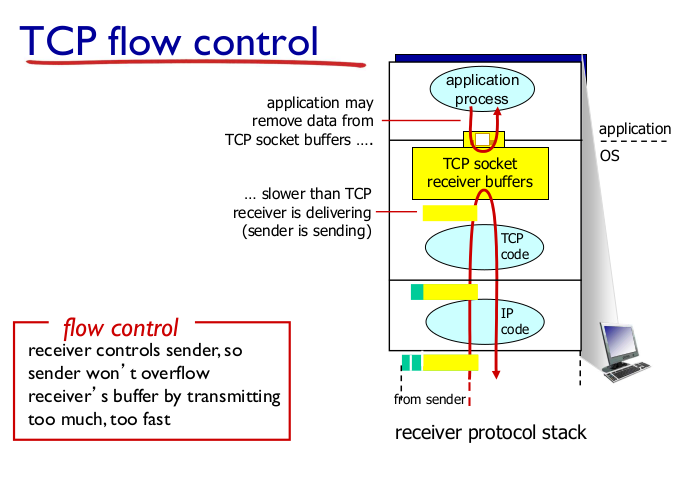
- (receiver control)
- sender의 buffer가 넘어가지 않도록 속도를 조절해서 보내는 것.
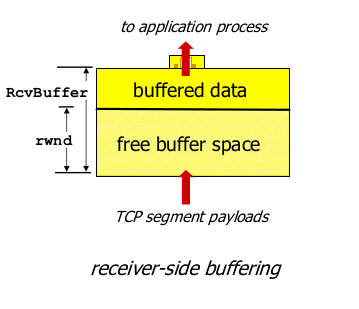
- rwnd: receive window, TCP header 값. 패킷 보낼때 마다 써서 보낸다.
- rwnd에 따라 조절해서 전송
connection management
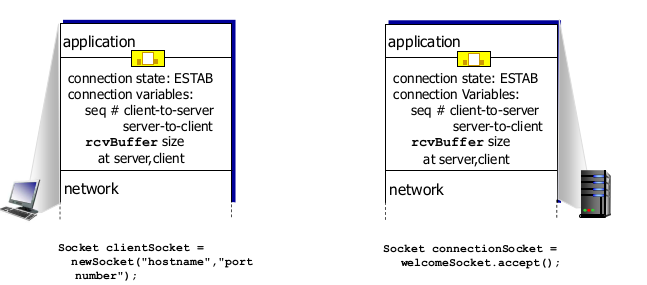
- sender와 receiver의 handshake
- connection을 맺으면서 seq, rcvBuffer
- 2-way handshake
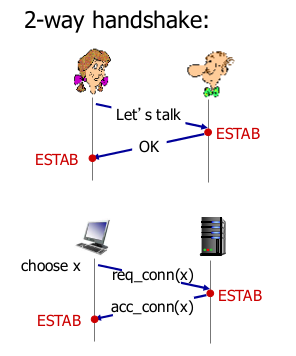
- 항상 잘 작동할까?
- variable delay
- message loss
- failure scenarios
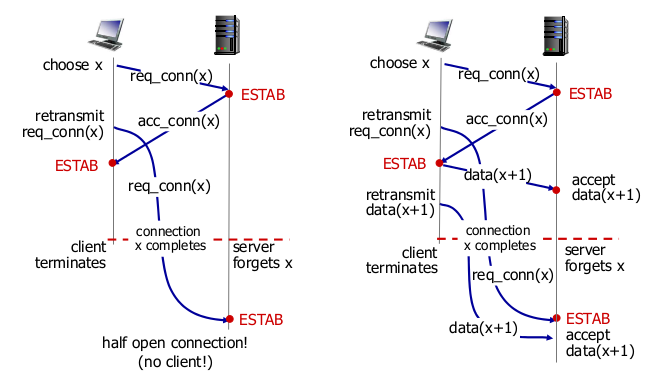
- 2way는 모자라다.
- 항상 잘 작동할까?
- 3-way handshake
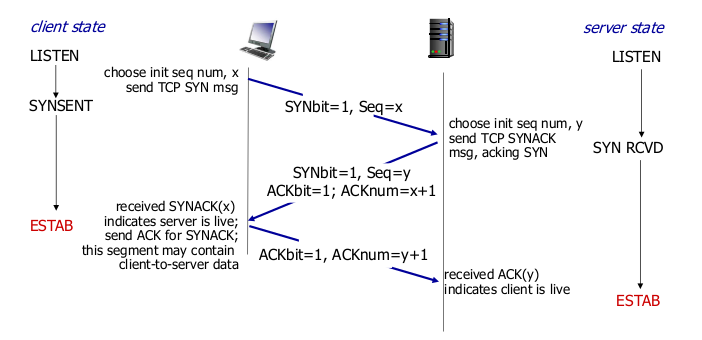
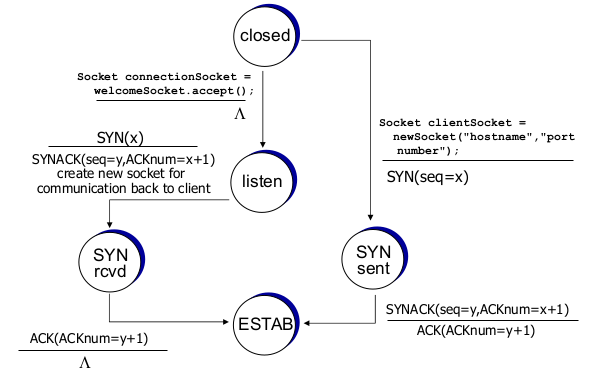
- TCP: closing connection
- 4-way handshake
- FIN bit가 1인 Segment를 보낸다.
- 받은 FIN에 ACK 응답
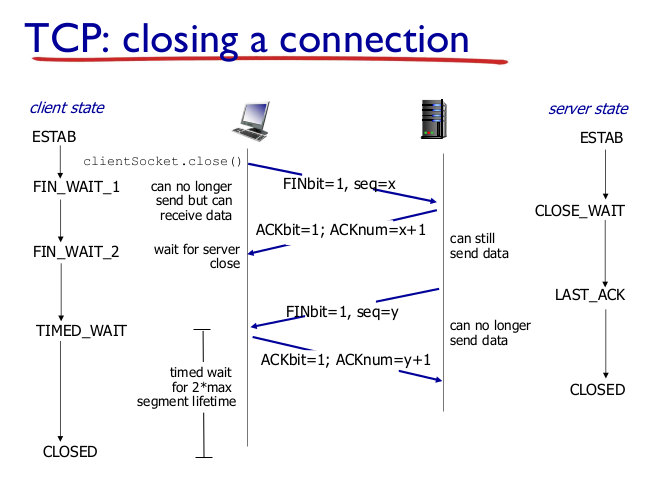
- 4-way handshake
6. principles of congestion control
패킷이 너무 많이 생겼을 때
RTT가 너무 많아졌을 때, 덜 만들자
- Congestion
- “source가 데이터를 너무 많이, 빨리 보내서 네트워크가 이를 처리하기 어려운 상태”
- flow control과는 다르다
- flow control: 상대방 버퍼 문제
- congestion control: 전체 데이터 문제
- manifestation
- lost packet (router-buffer overflow)
- long delay (router-buffer queueing)
- top-10 problem!
- delay가 커지고, loss가 커지면 congestion
- Scenario 1
- one router, infinite buffer
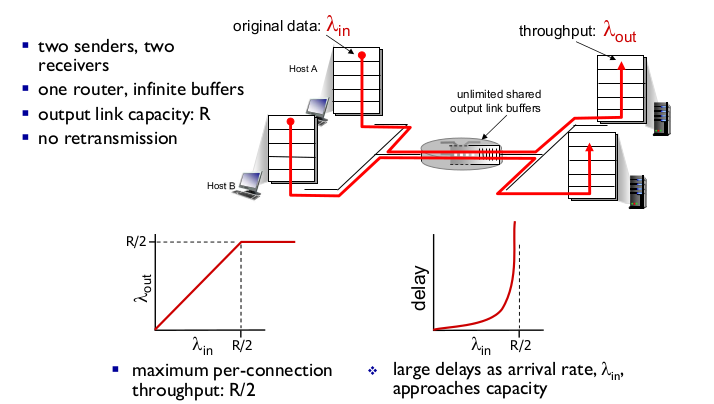
- one router, infinite buffer
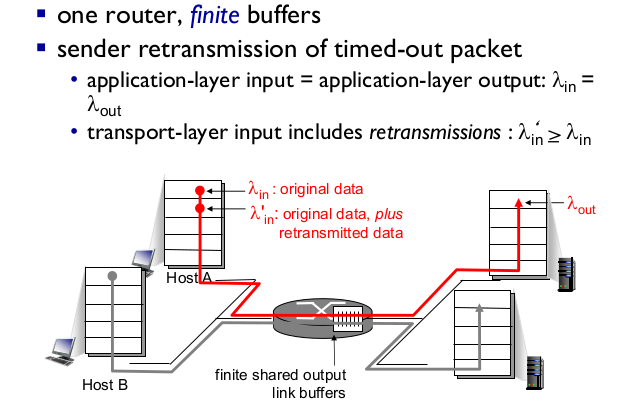
- Scenario 2
- one router, finite buffer
- Idealization: packet knowledge
- sender가 router가 available한 상태일 때만 전송한다.
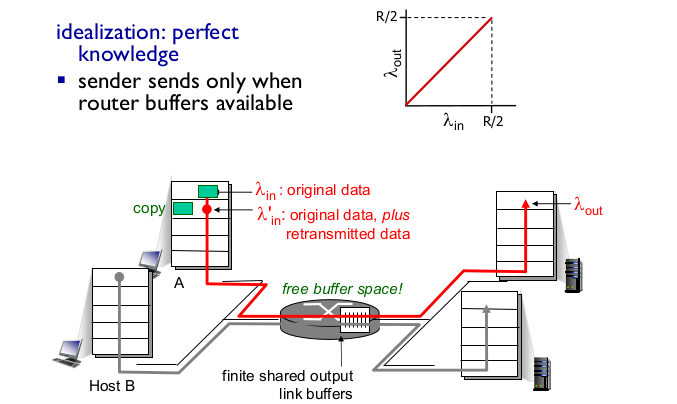
- sender가 router가 available한 상태일 때만 전송한다.
- Idealization: known loss
- sender가 패킷이 손실된 걸 알고 다시 보낸다.
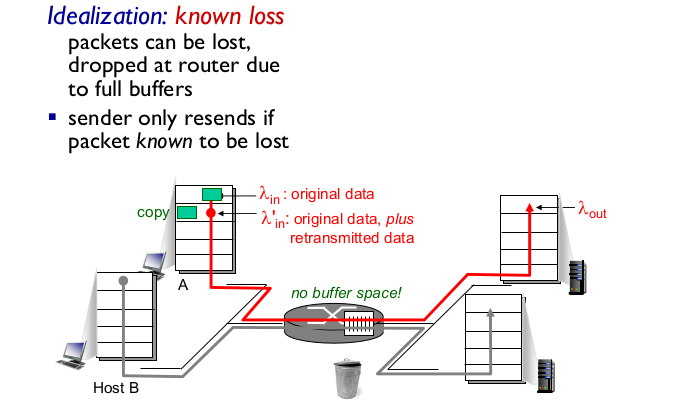
- sender가 패킷이 손실된 걸 알고 다시 보낸다.
- Realistic: duplication
- 패킷은 송실될 수 있고
- congestion
- 다시보낸 것까지 감안한 성능이 “good put”
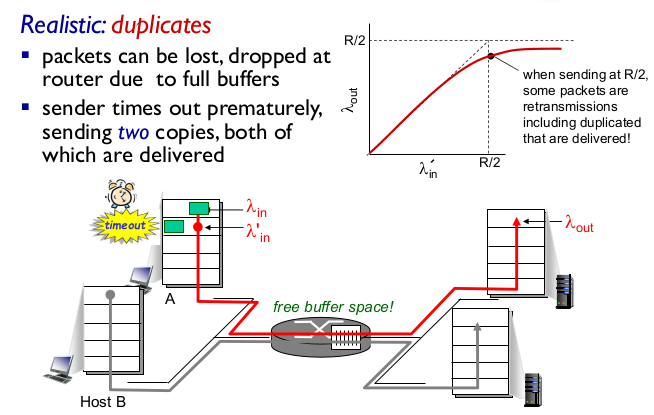
- 다시보낸 것까지 감안한 성능이 “good put”
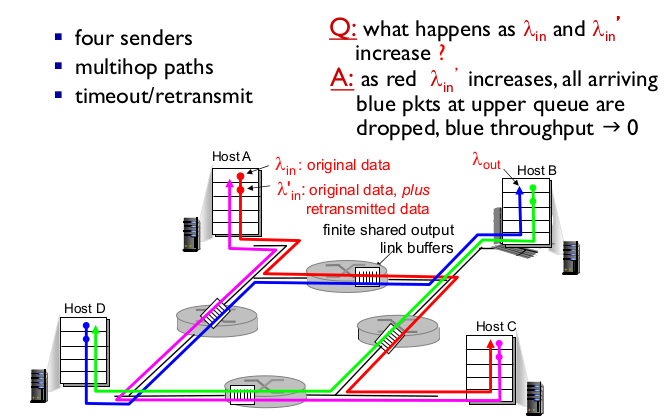
- one router, finite buffer
- Scenario 3
- sender 4개
- multihop paths
- timeout / retransmit
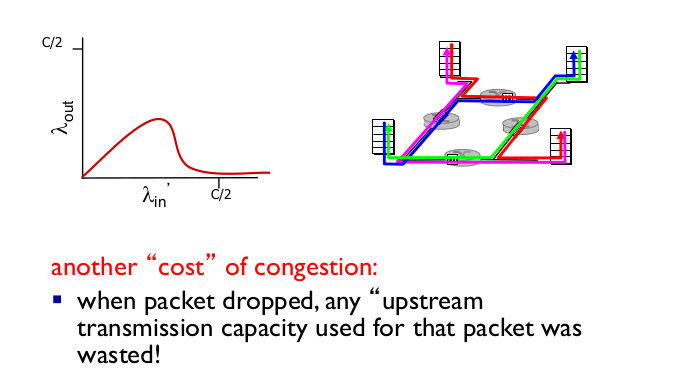
7. TCP congestion control
- additive increase, multiplicate decrease
- 증가할 땐 합 적용, 감소할땐 곱적용
- cwnd 1씩 증가: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -. … -> 99 -. 100
- cwnd 절반으로 감소: 100 -> 50 -> 25
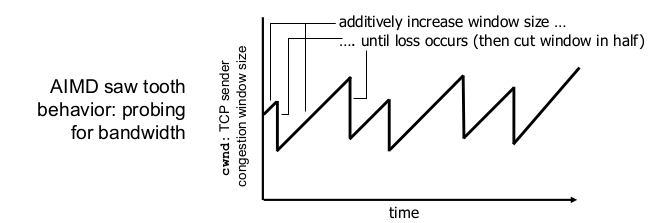
- cwnd deafult: 4096 -> 2048 -> 1024 ….
- TCP sending rate $$ rate ~~= cwnd/RTT (bytes / sec) $$
- 증가할 땐 합 적용, 감소할땐 곱적용
- TCP slow start
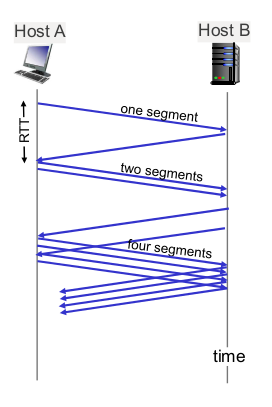
- initially cwnd = 1 MSS
- double cwnd every RTT
- 처음 rate는 slow, 점점 지수적 증가
- TCP: detecting, reacting to loss
- timeout이 걸린다:
- cwnd를 1로 셋팅 (반으로 줄이는 게 아니라)
- slot start
- TCP RENO: 똑같은 ACK가 3개 (중간에 몇개 빼먹었다)
- cwnd를 반으로
- TCP Tahoe: 항상 cwnd를 1로
- (timeout 이건, 중복 3개 ACK건)
- TCP: switching from slow start to CA (Congestion Avoidance)
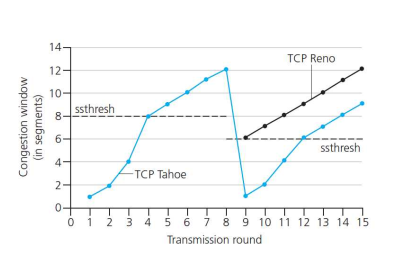
- variable ssthresth
- sshthresh 까지는 지수적으로 증가
- sshthresh 넘어가면 linear하게
- 문제가 발생하면 (timeout, duplicate ack 3)
- Tahoe에선 1
- RENO에선 반으로.
- sshthresh는 직전 cwnd의 절반
- variable ssthresth
- timeout이 걸린다:
- TCP throughput
- W: window size $$ (avg.TCP throughput) = 3/4*W/RTT (bytes/s) $$
Chapter 4: Network Layer: The Data plane
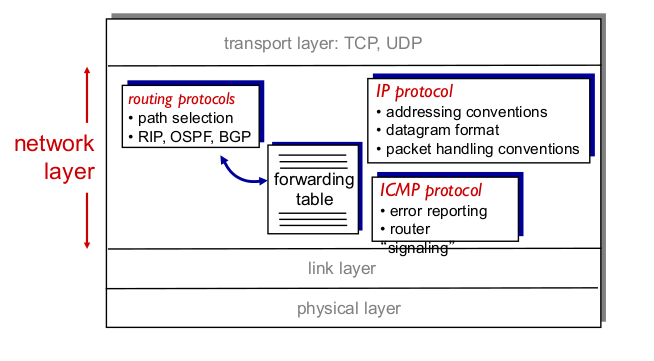
1. Overview of Network layer
- Network layer
- End-to-End
- 모든 router에 ip 가 필요 (switch, 기지국에는 필요없다)
- router는 header를 조사해서 next를 찾는다
- router별 network layer: routing table
- 기능
- Forwarding
- 다음번 hop을 찾아서 보내는 것
- Routing
- 길 찾기
- 최단 경로 찾기: routing alogrithm
- Forwarding
- Data plane
- forwarding 역할
- 다음 번 hop이 어디인가
- forwarding 역할
- Control plane
- 전체 routing algorithm 돌려서 경로설정
- Network-wide
- traditional routing algorithm: 라우터에 구현
- SDN: server에서 구현
- Per-router control plane
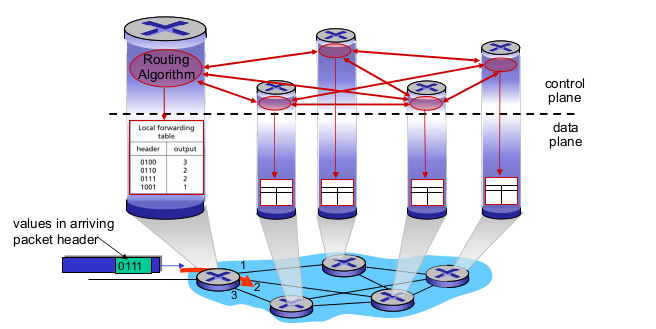
- 라우터마다 control plane
- 자기 라우팅은 자기가 계산
- 주기적으로 control plane 돌려서 routing table 갱신
- 기존 router에선 control plane, data plane이 분리되어 있지 않음
- Locally centralized control plane
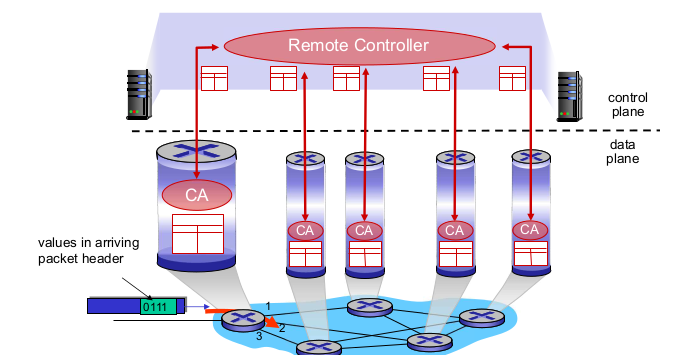
- 서버에서 라우팅 관리
- Network service model
- Sender와 receiver 사이의 channel 역할
- individual datagram services
- guaranteed delivery
- guaranteed delivery (< 40 ms delay)
- flow of datagram services
- in-order delivery
- guaranteed minimum bandwidth
- packet inter spacing: 어느정도 띄워서 보낸다
- 이런거 다 안된다! 오늘날 인터넷은 그저 best effort. guarantee는 없다.
2. What's inside a router
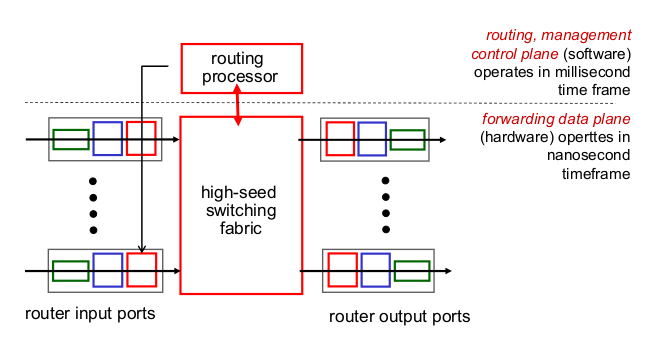
- Input port functions
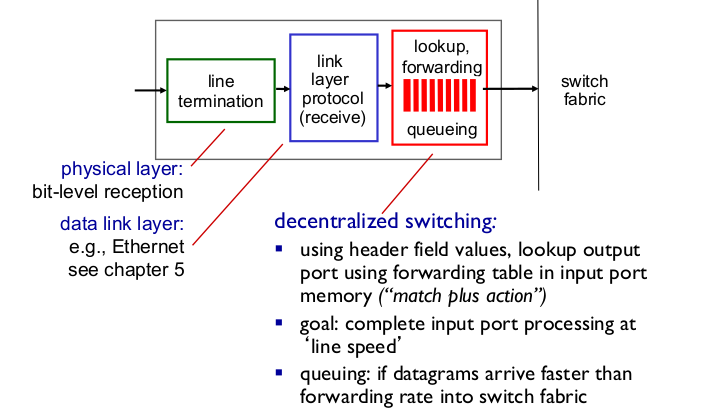
- line termination: physical layer
- link layer protocol: datalink layer
- lookup, forwarding: deccentralized switching
- ip header를 보고 “matching”, next hop을 찾고
- 목표: “line speed” processing
- queueing
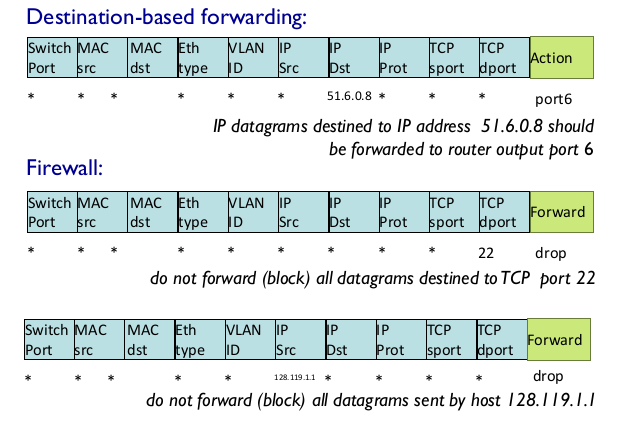
- destination-based forwarding: destination 주소만 본다 (traditional)
- generalized forwarding
- Destination-basesd forwarding
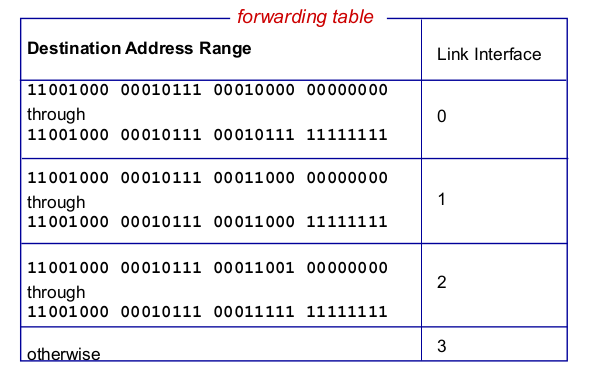
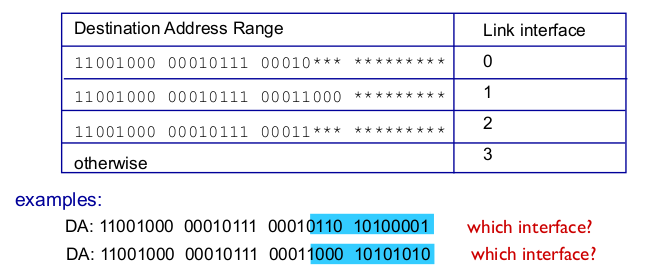
- longest prefix matching
- TCAM (ternary content addressable memories)
- matching 되는 컨탠츠로 찾겠다.
- ns 단위로 처리 가능
- content addressable
- TCAM (ternary content addressable memories)
- Switching fabrics
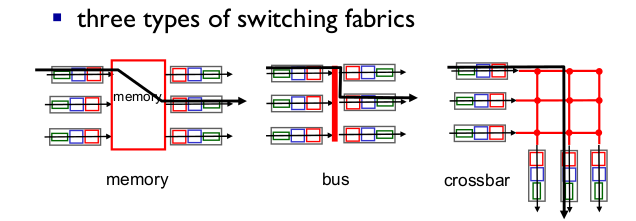
- switching rate: rate at which packets can be transfer from inputs to outputs
- longest prefix matching
- Switching via memory
- 1 세대.
- copy 때문에 느리다.
- Switching via a bus
- bus contention. 버스 성능에 따라 속도가 제한
- Cisco 5600: 32 Gbps bus. enterprise router로 충분
- Switching via interconnection network
- bus가 여러개: bus bandwidth limitation 극복
- banyan network (중요한 곳만 연결), crossbar, other interconnection nets
- Cisco 12000: 60Gbps. 망 연결할 때 많이 쓴다.
- KT 망 - KONKUK 망 - SK 망
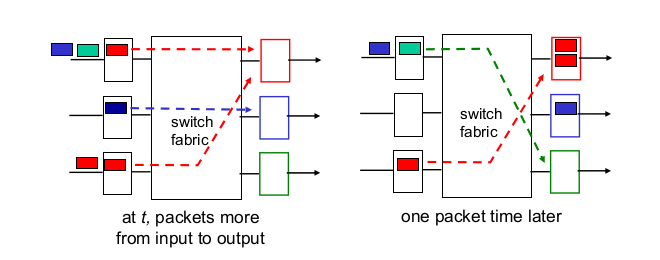
- Input port queueing
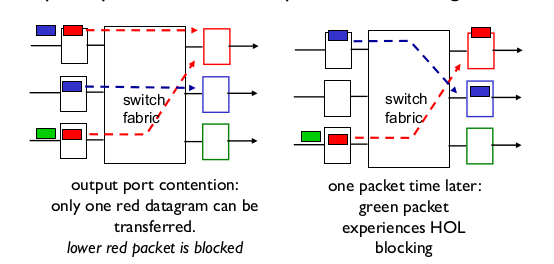
- HOL (Head of the line) Blocking: 큐의 처음 부분이 다른 애들이 나아가는걸 막는다.
- 보통 queueing을 한다고 하면 output port에만
- Output port
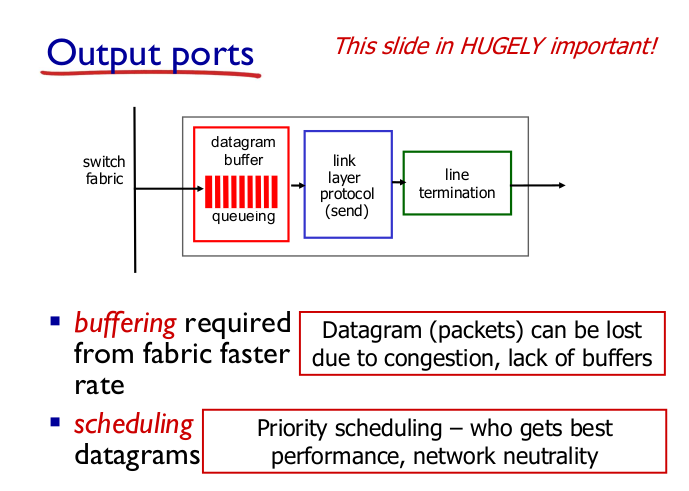
- HOL 문제 해결
- 주로 router/swtich.
- 보통 output port에 버퍼링한다.
- HOL 문제가 없어서 queuing delay가 훨씬 줄어든다.
- buffering을 얼마나 할 것인가?
- N: flow 포트 수. C: capacity $$ RTT * C / \sqrt(N) $$
- ex) RTT: 250ms, C = 10Gbps, N: 16 포트
- 계산결과: 2.5G bits ..?
- Scheduling mechanisms
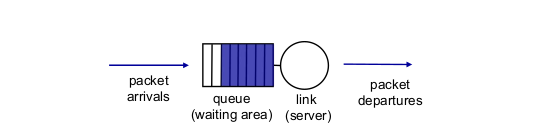
- scheduling. 큐가 여러개라면 어떤 패킷을 처리할 것인가
- FIFO scheduling
- 먼저 들어오는 패킷을 먼저 처리
- discard policy: 큐가 꽉 찼다면
- tail drop: 나중에 들어온거
- priority: 우선순위 낮은거
- random: 임의
- Scheduling policies: priority
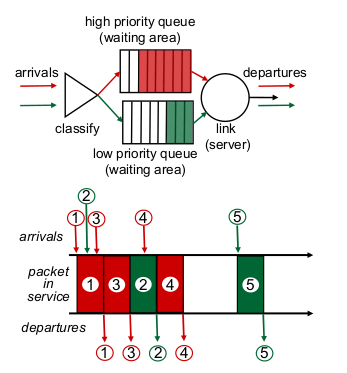
- multiple classes: 여러 priority. header에 marking 필요
- 비율을 잘 맞춰야 한다. high N개 할 때마다 low 1개씩.
- Round Robin (RR) scheduling:
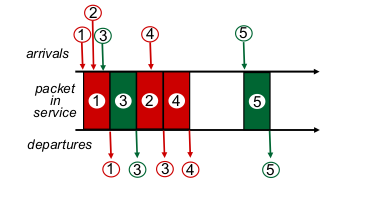
- 돌아가면서
- Weighted Fair Queueing (WFQ)
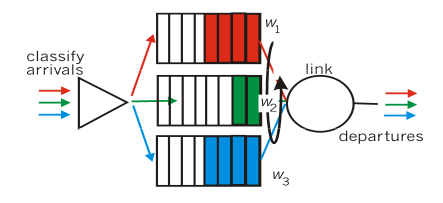
- Round Robin 일반화.
- highest: 3개씩
- middle: 2개씩
- lowest: 1개씩
- Round Robin 일반화.
3. IP: Internet Protocol
 best effort.
best effort.
- IP datagram format
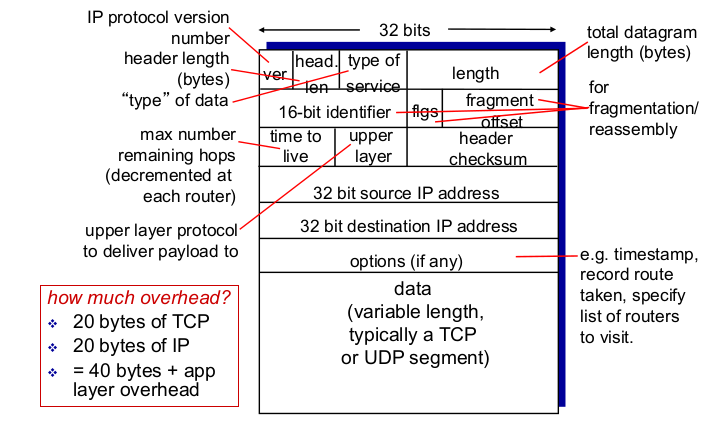
- length: $2^{16}$ = 64KB 최대.
- 16-bit identifier, fragment offset: MTU로 짜르고, 모은다
- upper layer: TCP, UDP
- TCP 20 bytes, IP 20 bytes, App layer overhead
- IP fragmentation, reassembly
- 패킷을 MTU 단위로 쪼개는 걸 fragmentation, 모으는 걸 reassemble
- identification, offset으로 모은다
- example
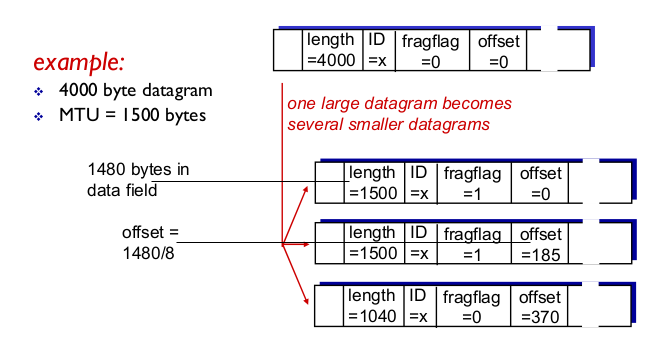
- offset은 octet단위
- IP addressing
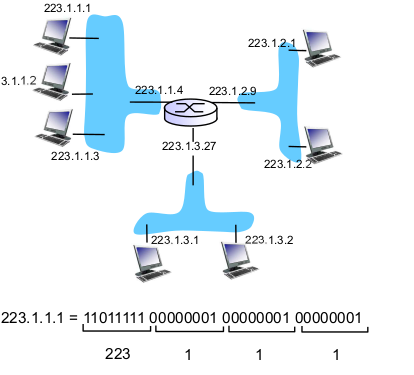
- IP: 32-bit identifier
- interface: connection between host/router and physical link
- IP주소는 매 인터페이스마다 할당
- subnet mask
- Subnets
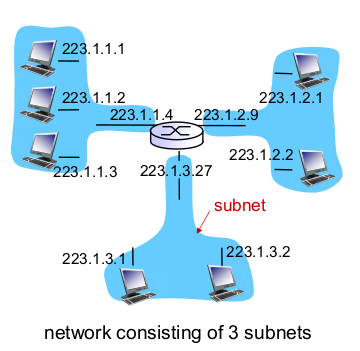
- IP address
- subnet part
- host part
- Subnet
- 라우터 거치지 않고 서로 접근 가능한 영역
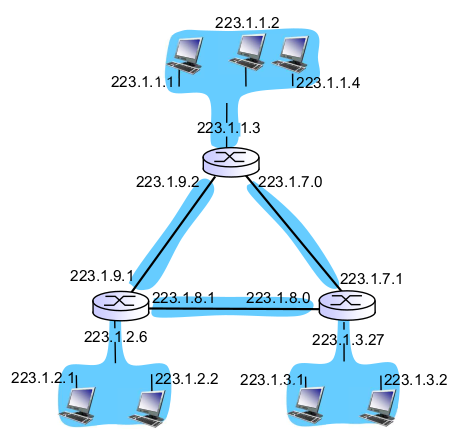
- 얘는 서브넷이 6개다.
- CIDR이 /30 이면 호스트가 2개 (00: network address, 11: broadcast address)
- 라우터 거치지 않고 서로 접근 가능한 영역
- CIDR: Classless InterDomaion Routing
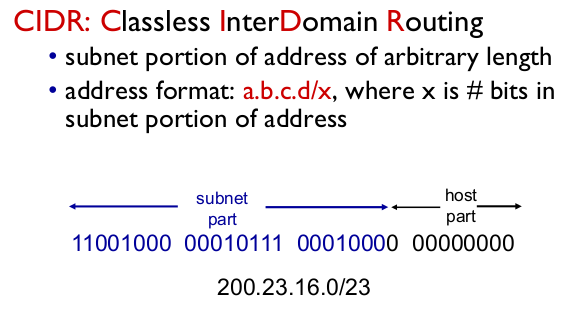
- CIDR로 라우팅테이블 크기를 줄일 수 있다.
- IP address
- IP addresses: how to get one?
- hard-coded by system admin in a file. 수동으로 파일에 박아 넣는다.
- Windows: control-panel …
- UNIX: /etc/rc.config
- DHCP
- dynamic 할당 / 반납
- renew 가능
- address 재사용 허용
- 더 많은 모바일 유저
- DHCP Overview
- host가 서브넷에 들어오면 “DHCP discover” broadcast
- DHCP server responds with “DHCP offer”
- host request “DHCP request”
- server sends address “DHCP ack”
- Well-known port: 68
- DHCP: more than IP address
- DHCP 는 IP address 할당 그 이상의 일을 한다
- router의 IP를 같이 준다
- DNS Server의 이름과 주소
- network mask
- DHCP: example
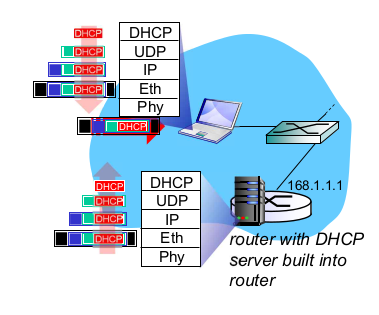
- laptop에서 필요한거: 자기 주소, DNS, router
- DHCP request: UDP, IP, Ehternet으로 encapsulate
- Ehternet frame은 LAN에서 broadcast
- 그러면 실제로 IP를 어디서 갖고오지?
- 한국: KRNIC.NET -> KT, SKT
- 전세계: ICANN
- How does an ISP get block of addresses?
- ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned
- allocates addresses
- manages DNS
- assgin domain names, resolve disputes
- hard-coded by system admin in a file. 수동으로 파일에 박아 넣는다.
- NAT: network address translation
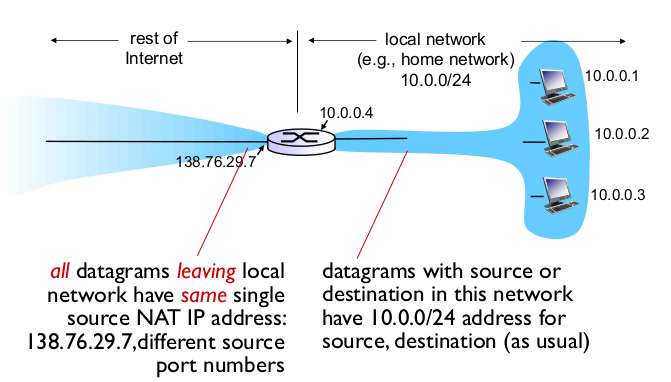
- single NAT IP address, different port -> different local addresses
- motivaltion
- 주소 1개를 여러 디바이스가 공유 (6만개)
- 로컬 네트워크에서 주소 변경
- 외부엔 알리지 않아도 된다
- ISP에 비해 편리하다
- 보안요소
- 디바이스가 바깥세상에서 Visible 하지 않으므로
- Implementation: NAT router
- outgoing datagrams replace
- (source IP, port) -> (NAT IP, new port)
- remember
- incoming datagrams replace (“NAT table”)
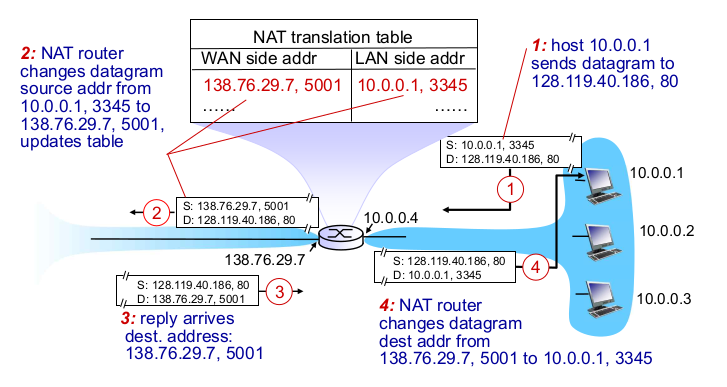
- 16-bit port-number field
- 단점
- router는 layer 3 까지만 처리해야한다.
- address 부족은 IPv6에서 해결되어야 한다.
- end-to-end 위반
- NAT는 중개자가 필요하다
- NAT traversal
- Server에 직접 연결하고 싶을 떈? 방법이 없다.
- outgoing datagrams replace
- IPv6
- motivation
- initial motivation: 32-bit address space가 모자르다
- additional motiviation (header)
- processing / forwarding speed up
- QoS
- IPv6 datagram format
- fixed-length 40 byte header
- 꼭 필요한 것만 있다
- option이 없다.
- fragmentation을 허용하지 않는다.
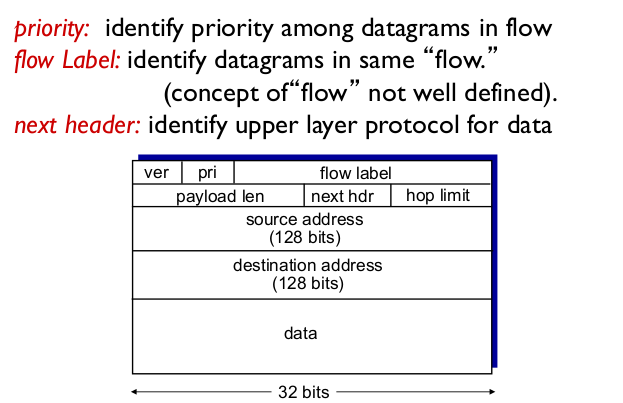
- flow label: QoS support
- flow 가 무엇인가. src ~ dest로 연속해서 만드는 패킷들의 집합 (stream). 아직 잘 정의되진 않음
- payload len: data length
- next hdr: UDP냐 TCP 등의 추가 header. Next hdr에서.
- hop limit: TTL reply 횟수
- IPv4옵션 (여기 routing 해라) 가 없다.
- fragmentaation, ID가 없다. flow label이 생김
- 단순화했음에도 헤더의 길이가 늘어났다. address가 32bits -> 128bits가 됐으므로
- Other changes from IPv4
- Checksum. 단순화 시키기 위해 삭제. 통신장비의 성능이 좋아져서 error도 적다. processing time을 줄이기 위해
- options: 허요, 하지만 Next header field에서.
- ICMPv6: new version of ICMP
- additional message type: “Packet Too Big”
- multicast group management functions
- Transition from IPv4 to IPv6.
- 사람들이 잘 안바꾼다.
- 동시에 모든 router를 upgrade할 수는 없다.
- no “flag days”
- IPv4와 IPv6를 같이
- Tunneling
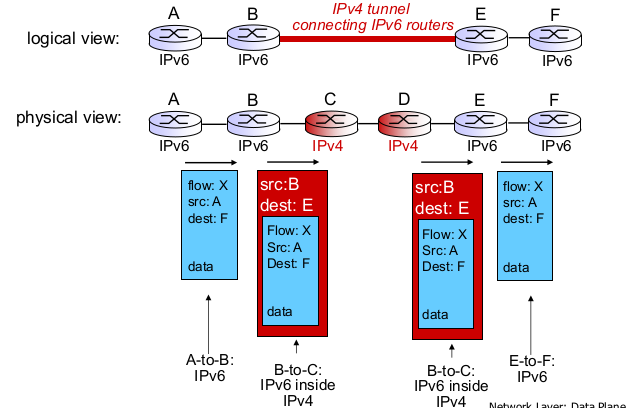
- IPv6 datagram을 IPv4 datagram payload로 전송
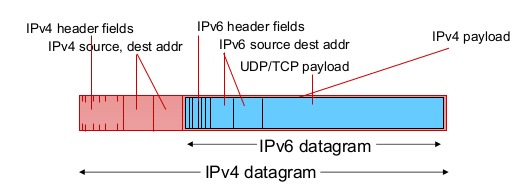
- IPv6 datagram을 IPv4 datagram payload로 전송
- IPv6: adoption
- 중국이 가장 많이 쓴다
- Google: 8%의 client
- NIST: 정부의 1/3 도메인
- 20년 정도 걸릴듯
- 20년간의 app 변경, WWW, Facebook, …
- motivation
4. Genralized Forward and SDN
SDN: Network 가상화 기술. (Software Defined Network)
각 라우터의 control 모듈을 중앙서버에 모아두었다.
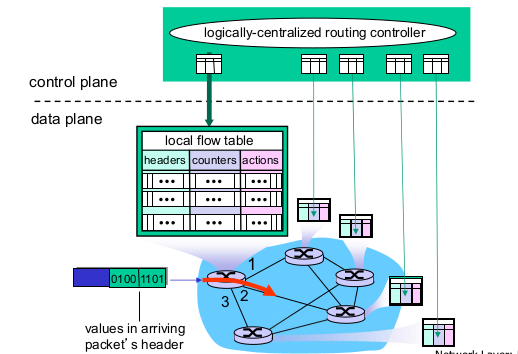 각 라우터 별 flow table이 있고, flow table을 주고 받는 프롵콜 OpenFlow가 있다.
각 라우터 별 flow table이 있고, flow table을 주고 받는 프롵콜 OpenFlow가 있다.
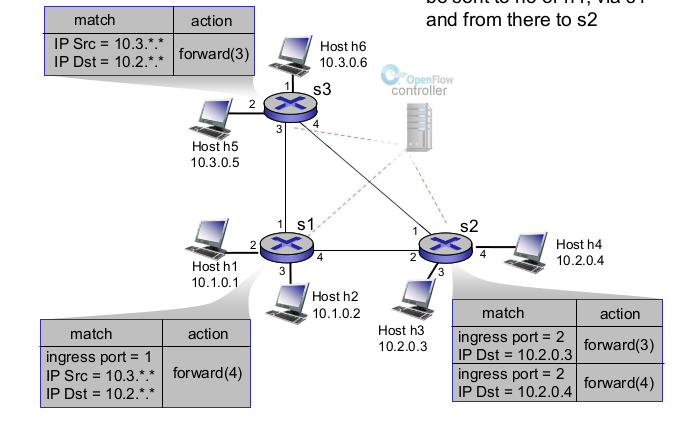
- OpenFlow data plane abstraction
- flow: 헤더 필드로 파악
- rules
- Pattern: 매칭, 목적지, 주소가 어디라면
- Actions: drop, forward, midify, 경우에 따라선 controller에게 보낸다
- Priority: 우선순위 높은 놈붙터 처리
- Counters: 통계. 매칭이 일어났을 때마다 +1
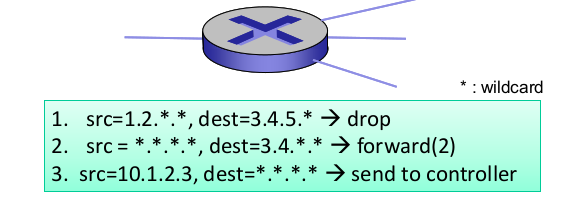
- OpenFlow: Flow table entries
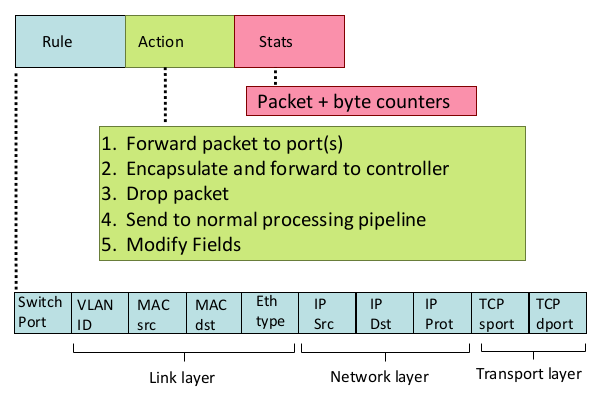
- OpenFLow abstraction
- match + action: match와 action으로 서비스 정의
- Router
- match: longest prefix
- action: forward
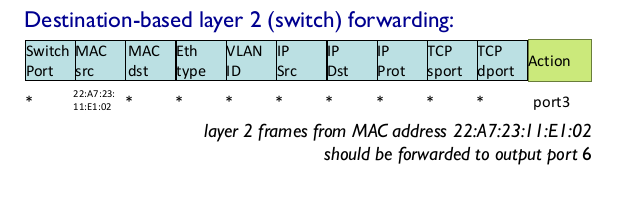
- Switch
- match: destination MAC
- action: forward or flood(broadcast)
- Firewall
- match: IP
- action: permit or deny
- NAT
- match: IP and port
- action: rewrite
- OpenFLow abstraction
Chapter 5: Network Layer: The control plane
Chapter Goals
- traditional routing algorithm
- SDN controllers
- Internet Control Message Protocol: ICMP
- network management: SNMP
- OSPF: routing algorithm, BGP, OpenFlow, ODL, ONOS, ICMP, SNMP
1. Introduction
- Network-layer functions
- forwarding: data plane
- routing: control plane
- Two approaches
- per-router control (traditional)
- logically centralized control (software defined networking)
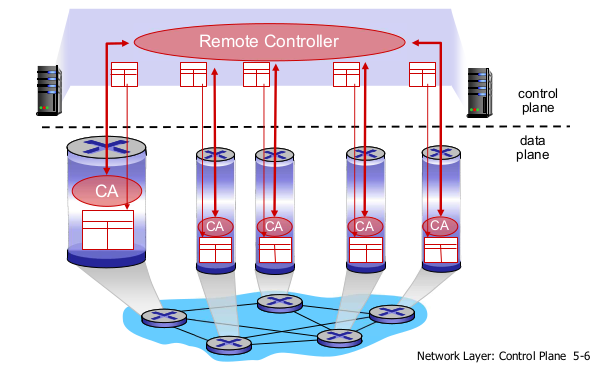
- Per-router control plane
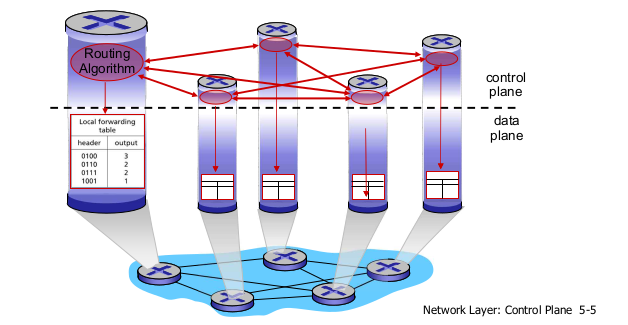
- Logically centralized control plane
2. Routing Protocols
- goal: “good” path를 결정한다.
- “good”: least cost, feastest, least congested
- routing: “top-10” challenge
- A link-state routing algorithm
- Dijkstra's algorithm
- 다익스트라.
- 모든 노드가 완벽한 정보를 알고 있다. (그래프 연결, 엣지간 코스트 등)
- 그걸로 각자 계산
- least cost path. 최소 경로를 찾자. 자기 자신부터 모든 노드까지
- k iteration
- notation
- C(x,y): x와 y 사이 cost
- D(v): source부터 v까지 현재 최솟값
- p(v): v까지 가는 경로의 직전 노드
- N`: 현재까지 계산한 것중 확정된 것. 더 이상 짧은 길이 존재하지 않는다.

- complexity
- $n(n+1)/2 = O(n^2)$
- 효율적인 구현: $O(nlogn)$
- link state는 모든 노드가 다 각자 완벽한 그래프 정보를 수집, 각자 계산
- 완벽한 정보를 수집하기 위해 broadcast
- 모든 정보가 교환될 떄 까지 계산 안하다가 한꺼번에 계산
- Dijkstra's algorithm
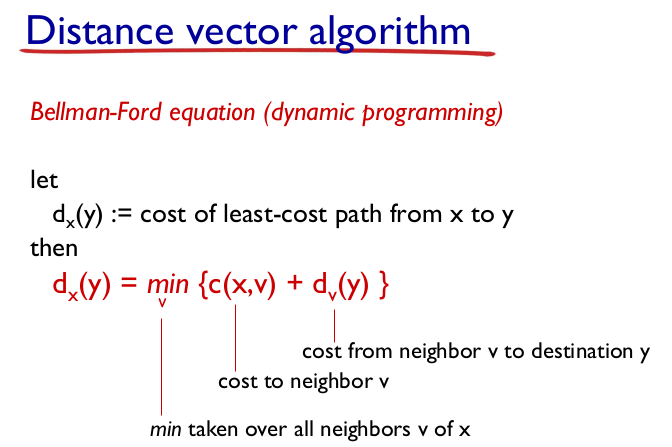
- Distance vector algorithm
- 이웃된 노드하고만 정보 교환
- k 번 정보교환으로 routing table 완성
- Bellman-ford
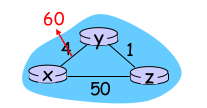
- distance vector가 단순하니까 많이 쓰지만
- 완벽한 정보를 모아서 계산하는게 아니라 현재 상태에서 계산.
- 실제로 라우터에선 RIP 하는 경우 30초마다 계산
- maximum hop count가 15라고 한다면 7.5분이 걸린다.
- 중간에 링크 1개가 끊어지면?
- 최정 경로 탐색까지 30초, 1분, 1분 30초, …. 걸리게 된다.
- 최정 경로 탐색까지 30초, 1분, 1분 30초, …. 걸리게 된다.
- Comparision of LS and DS algorithm
- message complexity
- LS: n 노드 수, e Edge 수 -> $O(nE)$
- DV: neighbor 끼리만 exchange. convergence time이 가변적.
- speed of convergence
- LS: $O(n^2)$ for $O(nE)$ messages
- DV: 가변적, LS보다 느리다
- robustness: router 하나가 고장나면?
- LS: 한꺼번에 broadcast
- 중간에 hacker가 개입하지 않도록 authentication 해야함
- DV: error propagate 에 시간이 많이 걸린다.
- LS: 한꺼번에 broadcast
- message complexity
3. Infra-AS routing in the Internet: OSPF
- Making routing scalable
- 망이 늘어남에 따라 목적지가 늘어난다.
- routing table size가 기하급수적으로 늘어나면 안된다.
- 어떻게 줄일까?
- 이상적
- 모든 router는 identical (똑같지 않다. 기관이 다르고 … 국가가 다르고 …)
- network “flat”
- scale: 도착지가 몇십억
- router에 모든 주소를 다 넣을 수 없다!
- administrative autonomy
- 망마다 자치
- internet: 네트워크의 네트워크
- 각 network admin, 기관마다 네트워크 알아서 해라. (너네는 DV 해라, 우리는 LS 하겠다.)
- Internet approach to scalable routing
- AS “autonomous systems”
- Infra-AS routing
- 기관 내 라이터들끼리 라우팅 프로토콜 알아서 해라
- Inter-AS routing
- 기관 별, 바깥 세상 라우터끼리 정보교환
- Interconnected ASes
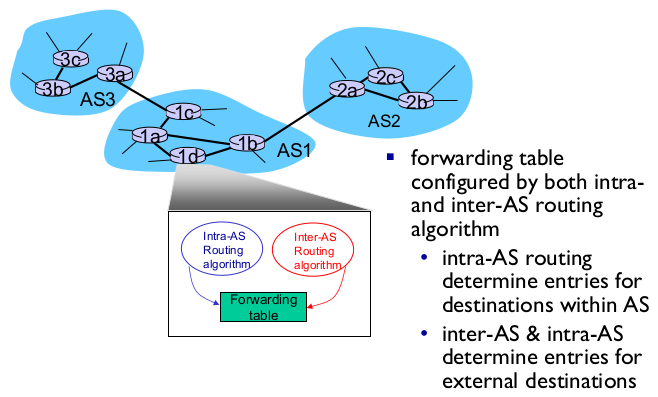
- Inter-AS tasks
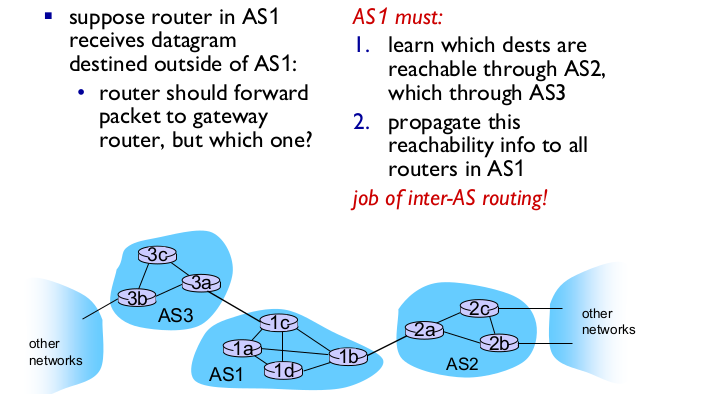
- 3a는 Intra-AS, Inter-AS 둘다 해야함.
- Inter-AS
- 3a->1c: AS3와 다른 네트워크 정보 전송
- 1c->3a: AS1, AS2, 그 외 네트워크 전보 3a에 전송
- Infra-AS
- 교환해서 자기만 갖고 있을 게 아니라 propagate 필요
- Intra-AS Routing
- IGP (Interior gateway protocols)
- intra-AS의 대표적 프로토콜
- RIP: DV, metric: hop count
- OSPF: Ls, metric: bandwidth/delay, metric이 단순 (IS-IS 존재)
- IGRP: cisco가 만든, OSPF에서 발전한 protocol. metric이 복잡하다.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
- “open”: 오픈소스다.
- link-state algorithm 사용
- link state broadcasting/flooding
- topology가 각 노드에
- 그래서 dijkstra로 shortest least cost path를 찾아낸다.
- flooding 한다.
- IP를 통해서 flooding 정보 공유 (TCP나 UDP를 쓰지않음.)
- link state
- Is-IS: OSPF랑 비숫
- OSPF “advanced” features
- security: authentication. (한 라우터가 잘못된 정보를 준다면 문제가 될 것.)
- multiple: same-cost paths 동일한 값 path 허용 => load balancing (RIP에선 단 1 경로)
- TOS 값에 따라 cost 측정 가능
- ex) satelite link 굉장히 느린데, 이메일 같은 건 이거 써도 됨.
- multicast 기능
- hierarchical OSPF
- 내부가 복잡하면 (건물 수십개) Flat보다 계층 라우팅이 효율적
- Hierarchical OSPF
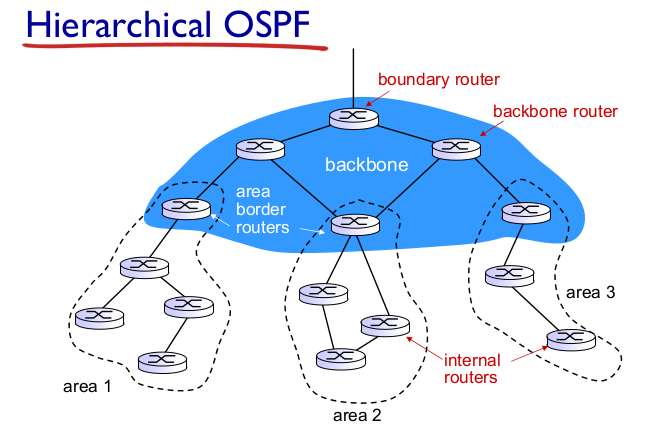
- area2 에서 area1 을 알 필요가 없다.
- area별 OSPF
- two-level hierarchy: local area, backbone
- link-state advertisements
- area border
- backbone routers
- boundary routers
4. routing among the ISPs: BGP
요즘 BGP 안쓰는 데가 없다.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
- 사실상 inter-domain routing protocol
- BGP provides
- eBGP: external BGP
- 나한테 주면 여기저기 보낼 수 있다는 AS정보를 받을 수 있다.
- iBGP: internal BGP
- 받은 reachability information을 내부 라우터에 전달. 이렇게 forwarding table을 만든다.
- BGP에서 중요한건 policy
- intra-routing protocol에선 최소비용이 중요
- inter-routing protocol에선 최소경로보다 “reachability”
- 그래서 reachability information 교환.
- 다른 네트워크에 “I am here"을 알려준다. 알려주지 않으면 reachability가 전달되지 않음.
- eBGP: external BGP
- eBGP, iBGP connections
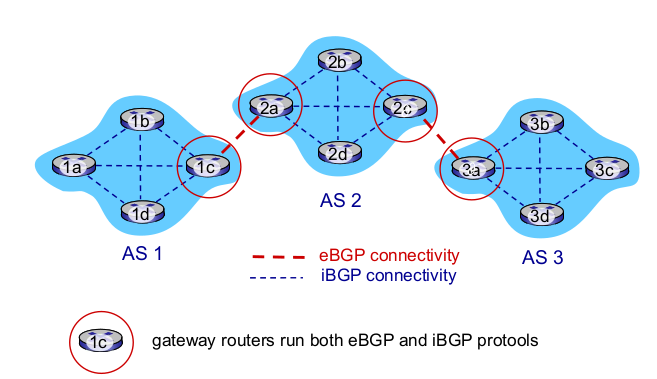
- BGP session: 두 BGP 라우터가 주기적으로 정보교환
- 1개의 session을 만든다.
- TCP connection으로 교환하는건 path vector
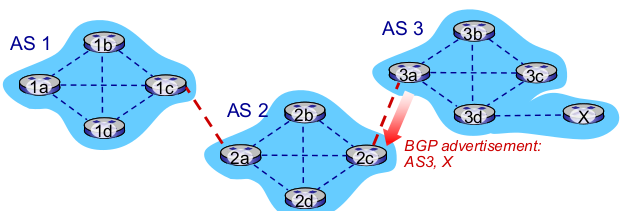
- AS 3, X 에게 보낼 수 있음을 알려줌
- Path attributes and BGP routes
- 서로 교환하는 reachability information
- prefix + “attributes” = “route”
- 어떤 네트워크 + attributes
- Attributes에는
- AS-PATH: 이러이러한 경로를 통해 X까지 보내주겠다.
- NEXT-HOP: 갈때 next hop이 뭐다.
- Policy-based routing
- 정책적으로 결정한 바에 의해 routing 해주겠다. (reachability가 있다 / 없다)
- 서로 교환하는 reachability information
- BGP session: 두 BGP 라우터가 주기적으로 정보교환
- BGP path advertisement
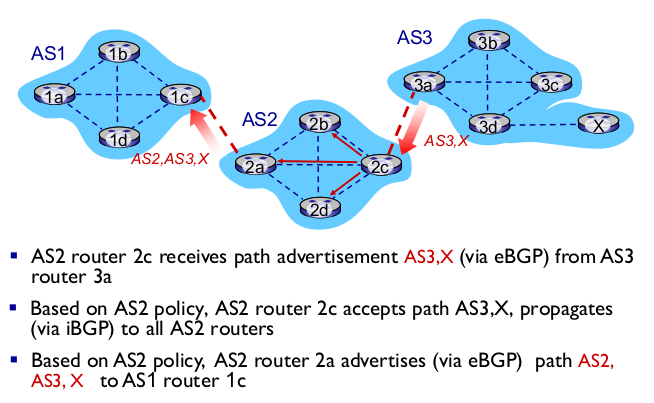
- BGP messages
- TCP 위에 connection 만들어서 정보 교환.
- OPEN: connection 만드는
- UPDATE: path. 새로운 경로를 알려준다. 또는 policy로 인해 withdraw
- KEEPALIVE: 계속 살린다
- NOTIFICATION: 에러 발생시 알려준다
- TCP 위에 connection 만들어서 정보 교환.
- BGP: achieving policy via advertisements
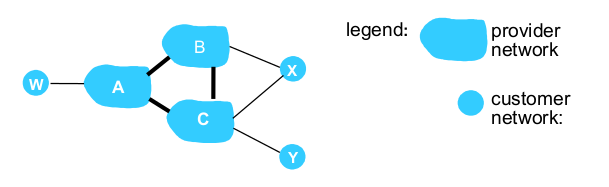
- BGP policy를 통해 transit traffic을 막을 수 있다.
- x: dual-homed. 2개 이상의 네트워크와 연결
- Why different Intra-, Inter-AS routing?
- policy
- scale
- hierarchical을 통해 scale할 수 있다
- performance
- Inter-AS에선 policy가 더 중요
5. SDN
기존 라우터에서 하던 RIP, IP, IS-IS 등의 프로토콜을 전부 다른 서버/클라우드에서 한다 (control plane). data plane에는 하드웨어 기계만.
“middlebox”: 다른 layer의 firewalls, load balancer, NAT boxes 등도 control plane에 존재 가능
최근 네트워크는 SDN. 이동통신사, Google
- Why a logically centralized control plane?
- avoid router misconfiguration, great flexibility
- control을 맘대로 고칠 수 있다.
- 기존 hardware-based 에선 Cisco, Huawei가 라우터 안고쳐주더라.
- table-based forwarding으로 프로그래밍이 가능해진다
- centralizzed easier
- distributed difficult: manufacturer가 입맞에 맞게 안고쳐주더라.
- open (non-proprietary)
- 소유권이 개방. module program들이 모두 옾느소ㅡ
- 비유
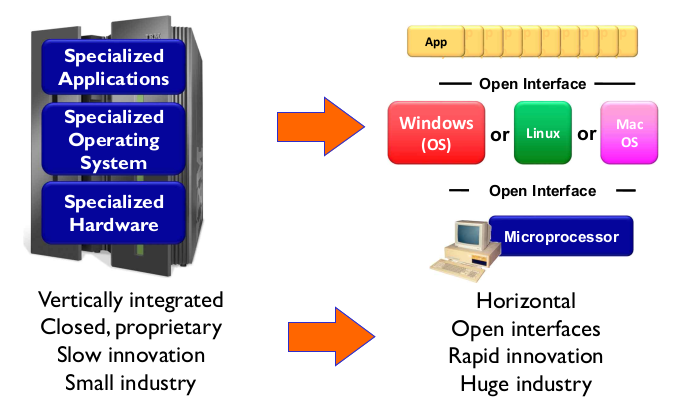
- avoid router misconfiguration, great flexibility
- Traffic engineering
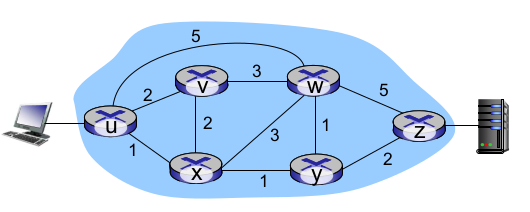
uxyz경로가 가장 빠른데, 로드밸런싱 목적으로 uvwz- SDN에서 traffic engineering하기 편하다.
- tradition에선 바꾸기 어렵다.
- SDN perspective: data plane switches
- Switch도 SDN 이용 가능
- SDN perspective: SDN controller
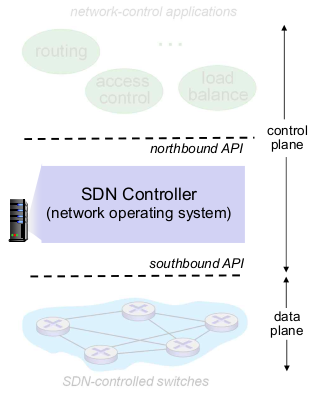
- southbound API: openflow
- northbound API: control plane은 controller가 필요
- Components of SDN controller
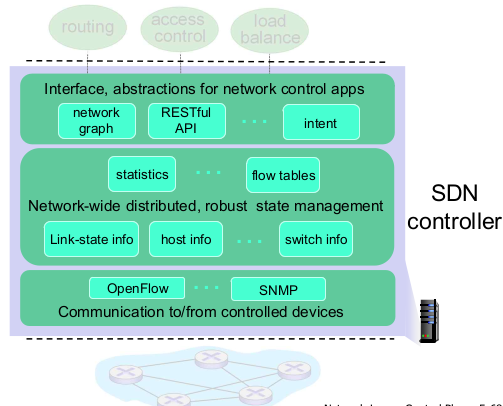
- RESTful API
- OpenFLow
- OpenFlow protocol
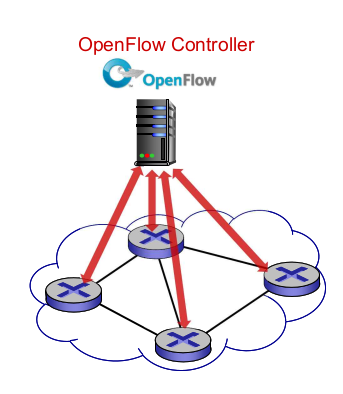
- controller와 스위치 사이 작동
- TCP 이용 + encryption
- 3가지 종류
- controller-to-switch
- asynchronous (switch-to-controller)
- 일방향. 문제발생 -> controller로 보낸다
- symmetric: 통계
- controller-to-swtich messages
- features: 스위치기능 query. 이때 switch reply
- configure
- modify-state: flow table operation
- packet-out: 에러처리? controller can send this packet out of specific switch port
- switch-to-controller
- packet-in: 처리 못하겠으면 controller에게
- flow-removed: 스위치에서 table entry가 삭제됐음을 보고
- port status: port 상태 변화 전송
- OpenDayloght (ODL) controller
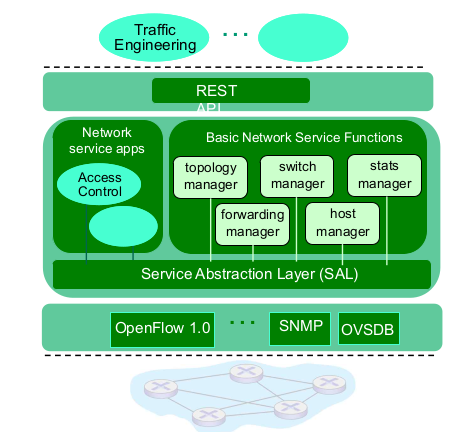
- ODL Lithium controller
- OpenFlow 1.0, SNMP
- RESTful API
- SAl, Network service apps 다 오픈소스다.
- ONOS controller
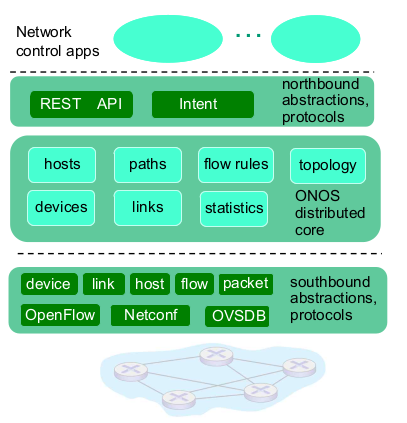
- 통신회사에서 많이씀.
- SDN challenges
- control plane: 잘 만들어야 한다. dependable , reliable 등등 골고루 잘 들어가야함
- rebustness to failures: 장애가 나더라도 잘 돌아가야한다.
- dependability, security
- networks
- ex) real-time, ultra-reliable, ultra-secure
6. ICMP: The Internet Control Message Protocol
에러가 나서 패킷을 버리게 되면 source에게 알려줘야 한다.
- ICMP: internet control message protocol
- Error reporting
- 이유를 알려줘야 한다.
- 이유를 알려줘야 한다.
- Echo -> ping
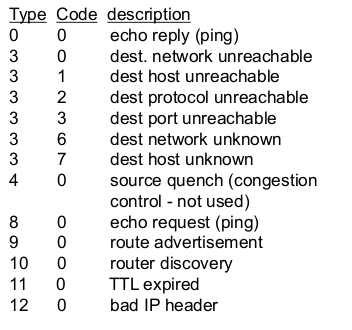
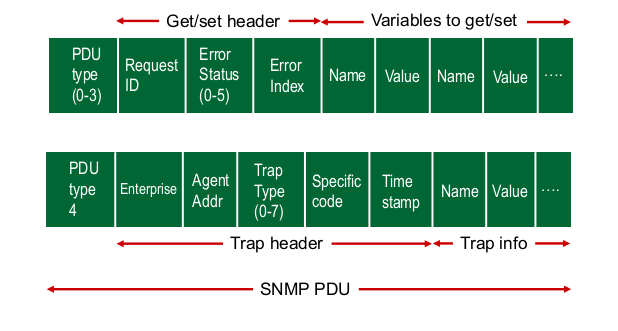
- ICMP message
- type + code + 버린 패킷 8 bytes
- Error reporting
- Traceroute and ICMP
- 첫 패킷은 TTL = 1 이걸 3번
- 다음은 TTL = 2 …
- TTL = n
- 중간에 어떤 node가 문제가 있는지 알 수 있다.
7. Network management and SNMP
- autonomous systems: 1000개 이상의 hardware / software
- 다른 복잡한 시스템: management가 필요
- Infrastructure for network management
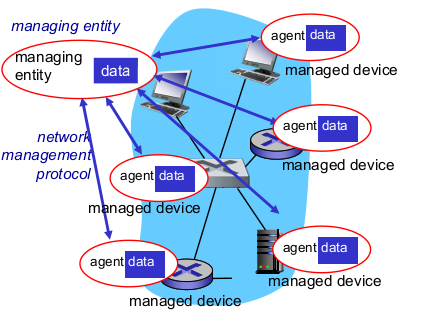
- managed device: 관리를 위한 MIB (Management Information Base)
- device 상태에 관한 Database
- Two ways
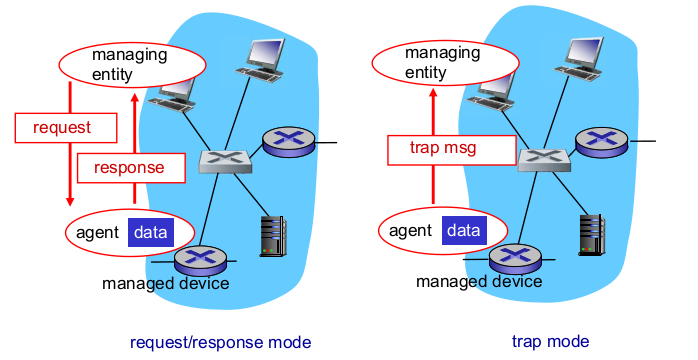
- message types
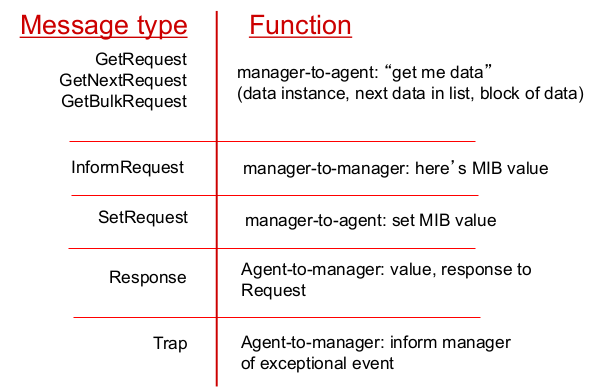
- message formats
6. The Link and LANs
- 원칙
- error detection, correction (transfer의 error는 end-to-end)
- 이웃된 노드 연결 - channel. channel을 sharing 할 수도 (공기, bus)
- link layer addressing: 48 bits
- local area network: Ethernet, VLAN. Ehternet은 WAN에서도 쓰인다.
1. Link layer: introduction
- terminology
- 이웃된 노드간의 프로토콜
- host-router, router-router
- 이웃된 노드간의 연결을 link라 한다.
- wired link: 유선. bandwidth 혼자 다 씀
- wireless link: 무선. 기지국과 단말기. 느리고, 공유. host는 많음
- datalink layer의 통신 단위는 frame
- network packet
- ip: datagram
- transport: stream (TCP), datagram (UDP)
- network packet
- data-link layer는 link로 연결된 물리적 이웃노드간 datagram을 전달해주는 역할 담당
- 이웃된 노드간의 프로토콜
- Link layer: context
- 다른 링크라면 다른 link protocol
- ex) ehternet, frame relay, 802.11
- 각 link protocol은 다른 서비스 제공
- reliable 혹은 reliabe하지 않음
- 다른 링크라면 다른 link protocol
- Link layer services
- framing
- network, ip에서 packet / datagram을 줬다.
- 이웃된 노드에게 전달해야한다.
- header와 trailer를 붙여서 framing, encapsulate
- shared medium이라면 누가 access하게 할 것인가.
- “MAC” 누가 매체를 차지하게 할 것인가.
- Medium Access Protocol. 이를 위한 주소 체계
- header에 source | destination
- 이웃된 노드 간 reliable delivery
- 3장에서 하는 법을 배웠다.
- low-bit error. (fiber, some twisted pair)
- wireless links
- high error rates
- 왜 end-to-end reliability와 link-level reliablity 둘다 하지?
- -> IP가 unreliable하다. 중간 router가 packet drop, 혹은 순서가 바뀔 수도
- 따라서 datalink에서 에러처리 해도 완벽하지 않다.
- flow control: 받는 놈이 받을 수 있을 만큼 준다
- error detection: reliable service를 위해, 1의 보수 checksum
- error correction: 다시 보내기, 중복해서 보내기
- half-duplex and full-duplex
- half-duplex: 양방향. 한순간에 한쪽만
- full-duplex: 양방향, 동싱통신
- framing
- Where is the link later implemented?
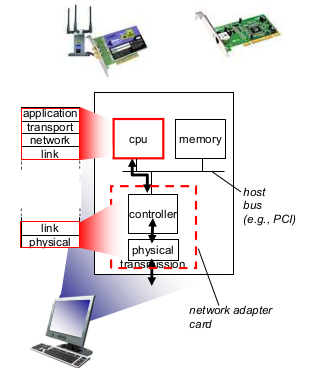
- LAN 카드. (또는 NIC 카드. Network Interface Card)
- 버스에 꼽혀있다.
- Ehternet card, 802.11 card, Ethernet chipset
- 카드니까 hardware + software + firmware
- Adaptors communicating
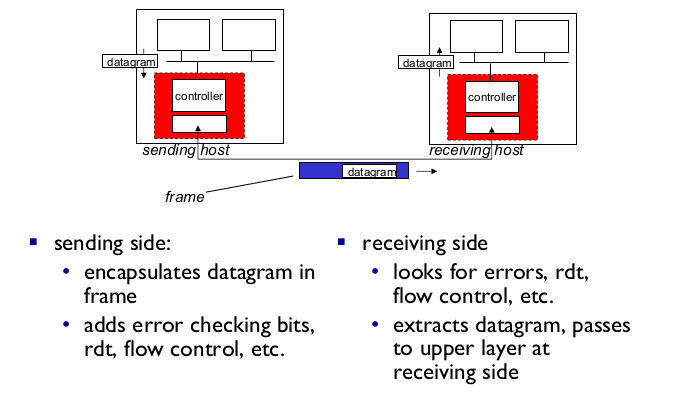
- sending side
- frame encapsulation: ip packet을 담는다
- header에 LAN 카드 주소, checking bits
- receiving side
- error control
- flow control
- error recovery
- sending side
2. Error detection
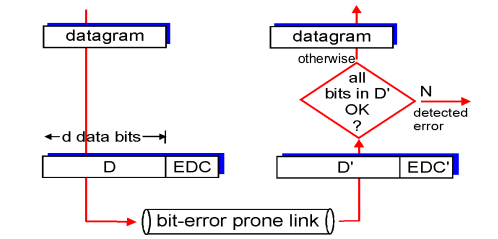 EDC 체크해서 계산값과 같으면 -> 에러 X, 다르면 -> 에러
EDC 체크해서 계산값과 같으면 -> 에러 X, 다르면 -> 에러
- Parity checking
- single bit parity

- 1 bit error를 감지
- odd number parity: 1의 갯수가 홀수인가
- even number parity: 1의 갯수가 짝수인가
- 비트가 2개 바뀌면 못잡아낸다
- two-dimensional bir parity
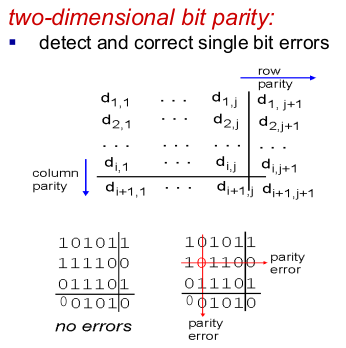
- 얘도 비트가 많이 틀리면 못잡아낸다.
- parity는 그냥 간단히 hardware 체크
- checksum을 많이 한다. UDP에서 했다.
- single bit parity
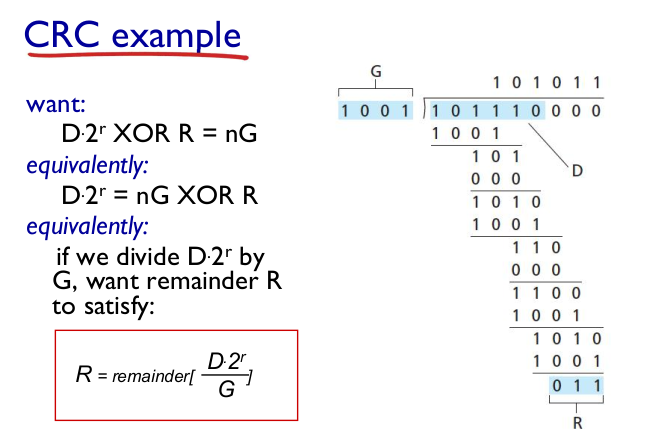
- Cyclic redundancy check (CRC)
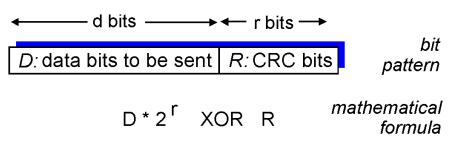
- 많이 쓴다.
- G: 양쪽 값이 고정된 값.
- $ D * 2^r \text{ XOR } R $ 값이 G로 나누어 떨어져야한다.
3. Multiple access protocols
매체를 공유할 때 (공기, 버스의 경우) 누가 매체를 차지하게 할 것인가
두 가지 link type
- point-to-point
- PPP
- point-to-point link between Ethernet switch, host
- broadcast (매체를 공유하고 있음)
- upstream HFC: cable TV. 동축케이블 공유
- 802.11 wifi
- 인공위성
- point-to-point
Multiple access protocols
- single shared broadcast channel
- channel을 sharing
- 경우에 따라 2개 이상의 노드가 전송을 하면
- 충돌 발생. 패킷이 개진다. 재전송이 필요해짐
- multiple access protocols. MAC protocol
- 분산 알고리즘이다.
- control signal을 보내는 채널이 따로 없다. (no out-of-band channel, coordination)
- channel communication은 알아서 해야한다.
- An ideal multiple access protocol
- 전체 channel capacity가 R bps 일때
- desiderata
- 노드가 1개라면 R을 다 쓸수 있다.
- 노드가 M개 있다고 하면 $R / M$ 만큼 갖게 해야함.
- fully decentralized
- 중앙 집중 노드가 없다. 알아서 해야한다.
- no synchronization of clocks, slots
- 단순할 수록 좋다.
- single shared broadcast channel
MAC protocols: taxonomy
- channel partitioning: channel을 나눠쓴다.
- TDMA: time division multiple access. 시간을 slot으로 나눠 쓴다.
- FDMA: frequency division multiple access. 주파수를 나눠서 사요
- CDMA: Code division multiple access. chipset이 각자 encoding
- random access
- 임의로 access. 충돌을 허용. recovery 방법 내장
- taking turns
- token 이 있어서 token 가진 애한테만 채널 사용
- 보낼 데이터가 많다면 혜택을 준다.
- channel partitioning: channel을 나눠쓴다.
Channel partitioning MAC protocols: TDMA
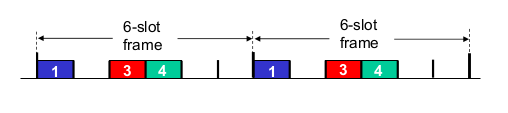
- TDMA: time division multiple slots
- 장점: 1slot만큼 bandwidth guarantee
- 단점: 안쓰는 애한테도 channel 할당
Channel partitioning MAC protocols: FDMA
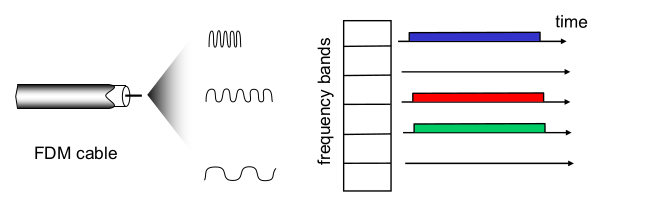
- FDMA: frequency division multiple access
- 동시에 다 보내기는 하지만 전체적인 bandwidth는 $ R/n $. 안쓰는 애 낭비
Random access protocols
- 누구든지 쓰고 싶을 때 써라. 몇가지 조건
- send 하려는 노드가 있으면
- R을 혼자 다 쓴다.
- 중앙집중 노드가 coordination 하지 않음. 알아서 분산
- 2개 이상의 노드가 전송 -> collision
- send 하려는 노드가 있으면
- random access protocol spec
- collision detect 방법이 있어야함.
- collision recover 방법이 있어야한다.
- examples
- slotted ALOHA
- ALOHA
- CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA
- 누구든지 쓰고 싶을 때 써라. 몇가지 조건
Slotted ALOHA
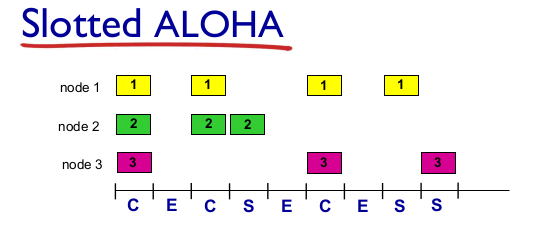
- 가정
- 모든 프레임은 동일한 크기
- time을 equal size slot으로 나눈다
- slot이 시작할 때만 보낸다.
- 시작할 때만 보내므로 동기화
- 동시에 2개 이상의 노드가 보내면 충돌.
- 모든 노드가 collision detect 가능
- Operation
- 보낼 데이터가 있으면 slot이 시작되는 시간까지 기다린다.
- collision detection.
- 가능하면 한다 -> Ethernet (CSMA/CD)
- ack 에러가 났다고 바로 보내면 다시 충돌. wait time 조절
- 못하면 acknowledgement (CSMA/CA)
- 온다: OK
- 안온다: 재전송
- 가능하면 한다 -> Ethernet (CSMA/CD)
- pros
- single active node가 channel을 다 쓸 수 있다.
- highly decentralized: node의 slot만 sync 필요
- simple
- cons
- collision이 일어나면 slot 낭비
- idel slot. 노는 slot이 있다.
- node들이 collision detect 방법을 알고 있어야한다.
- clock synchronization
- 가정
Slotted ALOHA: efficiency
- n개의 경쟁: $ p(1-p)^{N-1} $ 확률로 성공.
- MAX efficiency: $ Np(1-p)^{N-1} $
- P를 잘 조절했을 때 최대 $ 1/e ~= 0.37 $
- 37%의 효율
- 그대로 단순해서 많이 쓴다.
Pure (unslotted) ALOHA
- unslotted ALOHA: simpler, no synchronization
- 기다리지 않는다. 데이터가 있으면 바로 보낸다.
- 충돌이 훨씬 많이 일어 날 것.
Pure ALOHA efficiency
- $ p(1-p)^{N-1}(1-p)^{N-1} $
- $ = p(1-p)^{@(N-1)} $
- $ 1/2e ~= 18% $
- Slotted ALOHA보다 효율이 나쁘다.
CSMA (carrier sense mutliple access)
- CSMA: listen before transmit
- 보내기전에 채널, bus를 확인, 아무도 안보내면 내가 보낸다
- channel을 sense해보면, 보내고 있을 때 전압이나 전류가 다르다.
- idel일 때만 보낸다.
- busy할때는 기다린다.
- CSMA collisions
- 여전히 collision은 발생
- 거리가 있고, propagation delay가 있으므로
- CSMA/CD (collision detection)
- CSMA/CD: mechanism이 있다.
- 보내놓고 충돌이 일어나는지 확인
- 일어나면, 송신 중단 (재밍) 하고 나중에 아무도 안보낼 때 다시 보낸다.
- Ethernet CSMA/CD algorithm
- 충돌이 일어나고, 나중에 아무도 안보내서 다시 보냈더니 또 충돌이 일어날 수 있다.
- binary backoff: $ 0 < w < 2^{J} $인 난수 w, 여기서 J는 충돌횟수.
- efficiency
$$ efficiency = 1 / (1 + 5t(prop)/t(trans))$$
- ALOHA보다 훨씬 좋다.
“Taking turns” MAC protocols
- channel partitioning MAC protocosl
- 시분할 / 주파수 분할 / 코드분할
- $1/N$
- random access MAC protocosl
- low load: single node가 channel 다 쓰는게 가능
- high load: collision이 자주 일어나면 overhead
- “taking turns” protocols
- token등으로 돌아가면서 쓰게 한다.
- channel partitioning MAC protocosl
polling
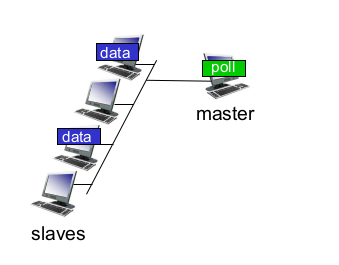
- master: control signal
- slave: 지시받은 대로 행동
- concerns
- polling overhead: 일일히 물어봐야한다.
- latency: 통신하는 데 걸리는 시간
- SPoF (master)
token passing
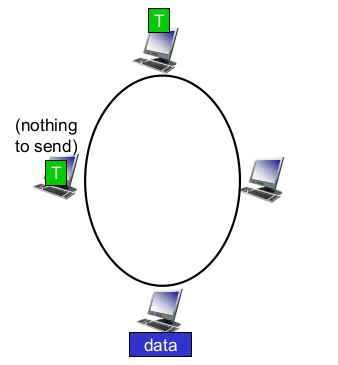
- node끼리 token 전달
- token있는 동안 데이터 전송 가능
Cable access network
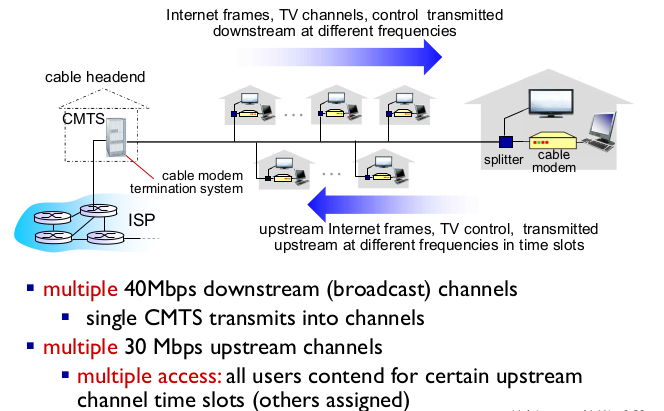
- 이미 있는 cable network를 통해 인터넷을 한다.
- spliter: downstream 데이터를 보고 cable TV 신호면 TV로, 인터넷 신호면 modem으로
- cable network로 Internet frame, 케이블 TV chanelm, control.
- downstream만 있는게 아니고, upstream 도 있다
- internet frame
- TV remote control signal
- control signal
- downstream, upstream 주파수 대역이 다르다.
- downstream이 upstream보다 훨씬 빨라야 한다. 트래픽이 많을 것이므로
- multiple downstream 40Mbps, single CMTS가 40Mbps를 나눠서 전송
- multiple upstream 30Mbps. upstream 데이터가 적으모로 모든 유저가 channel을 time slot으로 경쟁
- cable
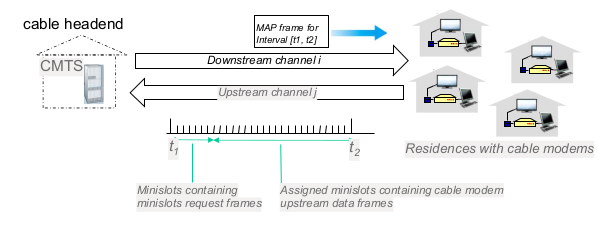
- 기본적으로 FDM: upstream, downstream 모두 주파수 분할해서 쓴다
- 경우에따라 TDP upstream: 데이터가 downstream에 비해 많지 않으므로 time slot 경쟁
CSMA/CA
- 무선에선 Collision Detection 불가.
- 멀리 가면 signal이 약해진다. collision이 일어나도 감지 불가
- Collision Avoidance한다.
Taking turns
- Polling from control: Bluetooth
- Token passign: FDDI, token ring
4. LANs
data link layer와 physical layer를 포함한다. (2개를 cover한다.)
link layer를 또 2개로 나눈다: MAC, LLC (logical link control)
LAN에서도 addressing한다. 48bits
ARP, Address Resolution Protocol
Ethernet 주소는 hardware board에 찍혀있다.
자신의 IP는 쉽게 알 수 있다. 상대방의 주소는? IP는 알 수 있는데, Ethernet을 알려면 ARP 필요
Switch: 가장 유명한 link layer 장비
VLAN: 가상화
- Addressing
- 32-bit IP address:
- network-layer 주소 체계
- host를 찾을 땐 ip 주소로
- application 찾아갈 땐 transport layer 16 bits port number
- MAC (or LAN, Ehternet, physcial) address:
- 48 bit 주소
- LAN 카드에 찍혀있다
- 1A-2F-BB-76-09-AD
- ISP가 바뀌면 IP가 바뀌는데, MAC은 flat하다. (게층적이지 않음)
- LAN address and ARP
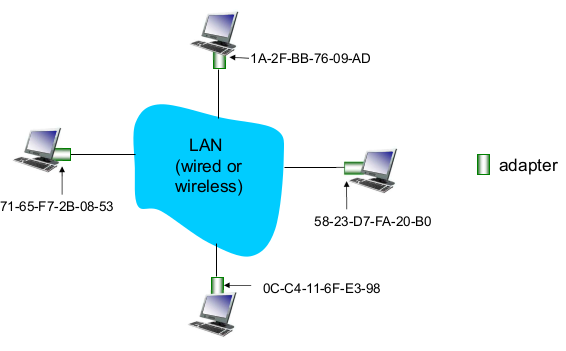
- LAN카드에 고유의 MAC주소가 찍혀있다
- 서로 통신하려면 IP주소 또는 MAC주소를 알고 있어야 한다.
- LAN 주소
- MAC 주소는 IEEE에서 관리
- 회사가 IEEE에서 MAC주소를 받아서 장사한다.
- 전세계에서 unique
- 비유
- MAC주소: 주민등록번호
- IP: 우편번호
- flat address -> 이전되도 MAC은 안바뀐다. portability 우수
- IP주소는 해당 네트워크에서 IPfmf qkedkdigka
- 계층적: subnet과 host
- ARP: address resolution protocol
- IP는 DNS라던가 cache로 알아낸다.
- LAN카드 주소는? ARP로 물어본다.
- 매 호스트마다 ARP table이 있어야한다, soft state: TTL 덕분에 시간 지나면 지워진다.
IP | MAC | TTL - ARP broadcast: FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
- 자기 Ethernet, IP address를 뿌릴것
- 상대가 받아서 응답. 서로 ARP table update
- “plug-and-play”: 별도의 설정 없이 LAN카드가 알아서 다 한다.
- Addressing: routing to another LAN
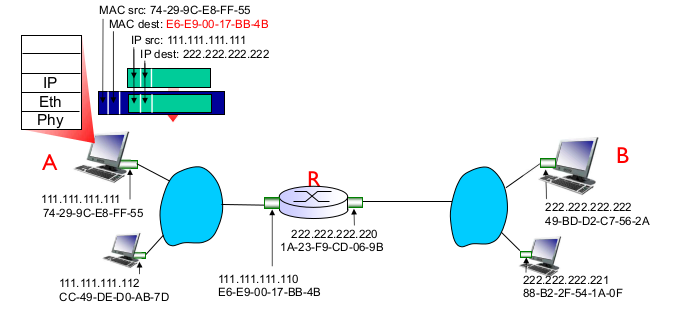
- 같은 LAN이면 ARP, Ethernet 주소를 알게 된다.
- A에서 B로 통신하려면?
- B의 Ethernet 주소를 모른다.
- next hop인 router의 LAN카드 주소를 써서 보낸다.
- 32-bit IP address:
- Ethernet
- token ring, FDDI, … 중에서 Ethernet이 이겼다.
- chip 하나로 구현, multiple speeds. 10M에 연결하면 10M, 1G에 연결하면 1G
- 인터넷 초창기부터 쓰이고
- 단순, 싸다
- speed가 10Mbps ~ 10Gbps

- bus broadcast
- CS해도 collision overhead
- 요즘은 Media sharing 하지 않음.
- 스위치구조를 bus가 아닌 crossbar로, CSMA/CD하면 충돌 안일어난다.
- physical topology
- bus: 90년대 많이 씀
- star: 오늘날, switch 형태. CSMA/CD까지 하면 진짜 충돌 안일어난다.
- bus: 90년대 많이 씀
- Ethernet frame structure

- preamble
- synchronization 하기 위함
- 10101010으로 7bytes, 10101011로 마지막 1byte
- 이 패턴이 시작되면 프레임이 시작되는 걸 알 수 있다.
- clock sync도 하고, 프레임 감지
- addresses: source, destination MAC 주소
- dest부터 시작하고 source가 있음
- type: 대부분 IP지만, Novell IPX, AppleTalk등 있음
- CRC: cyclic redundancy check
- error detect: 에러나면 drop
- preamble
- Ethernet: unreliable, connectionless
- 요즘은 에러가 정말 안난다.
- 하지만 에러가 나면 에러처리 안하고 drop
- LAN 중 대부분 conectionless
- connection 만드는 LAN: ATM
- connectionless: handshaking 안한다. 데이터 있으면 보낸다.
- unreliable: error가 있으면 drop
- 에러나면 처리는 TCP 아니면 Applicatio, 또는 안하던가
- MAC protocol은 CSMA/CD, 에러나면 binary backoff
- 802.3 ethernet standards: link & physcial layer
- 802.3: CSMA/CD
- MAC 위의 LLC는 생략되어 있다.
- differnet speeds: 2Mbps, 10Mpbs, 100Mbps, 10Gbps…
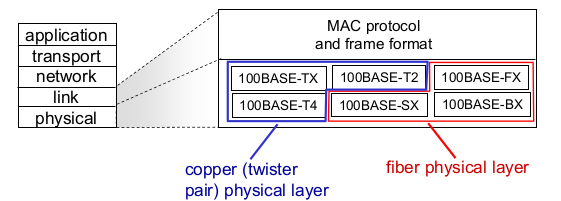
- MAC protocol: ATM, token ring, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA
- Physical
- 앞 숫자가 속도. 100BASE-Tx -> 100Mbps
- T: Twisted pair, F: Fiber
- Ethernet switch
- link-layer device
- 자기 포트로 오는 frame을 조사해서 MAC주소를 보고 다른 곳으로 전달
- Bus건 Switch건 CSMA/CD
- 물론 Switch의 경우 collision이 일어나지 않음. 다른 장비 호환성을 위해.
- transparent
- host는 switch가 있는지 없는지 모른다.
- plug-and-play
- configure할 필요 없다.
- switch: multiple simulateneous transmissions
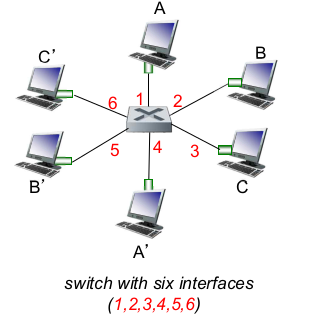
- A->A`, B->B`가 동시에 발생해도 충돌이 일어나지 않는다.
- switch: self-learning
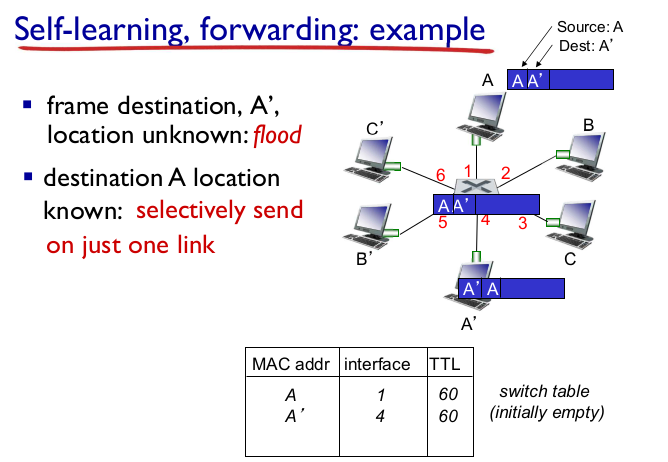
- Interconnecting switches
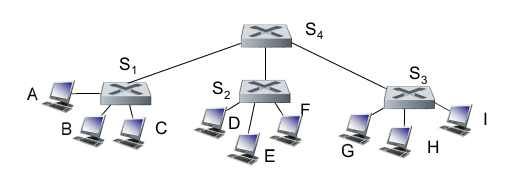
- 매 스위치마다 self-learning
- Institutional network
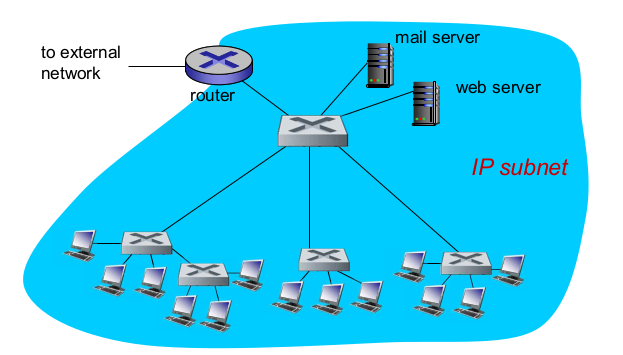
- Switches vs router
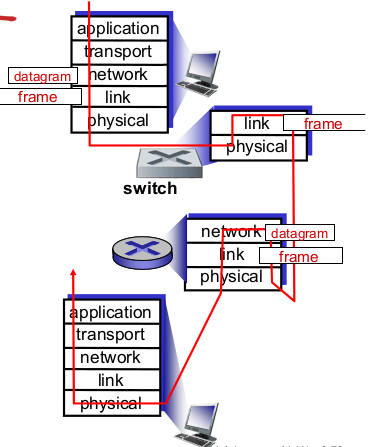
- VLANs
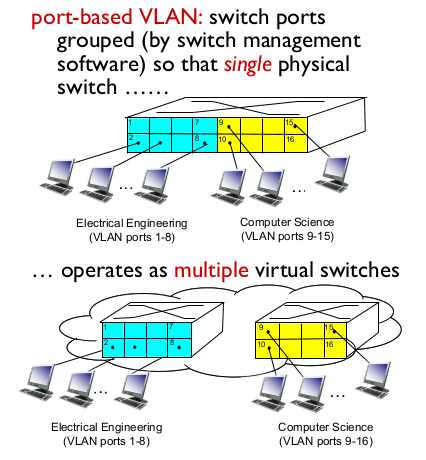
- port-based VLAN
- 물리적으로 1개의 switch
- 논리적으로 2개의 switch
- traffic isolation 된다
- router에서 물리적 2개의 switch가 연결된 것 처럼 가능
- port-based VLAN
- VLANS spanning multiple switches
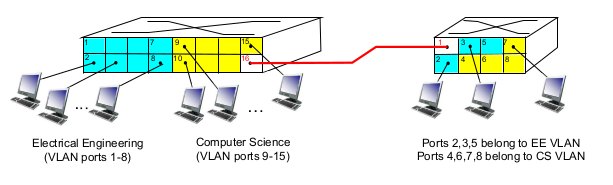
- 포트는 16개. 조직이 커지면 switch 1개 더 연결
- 논리적으로 1개의 switch
- VLAN 할땐 VLAN ID를 쓴다.
- 2개 LAN 연결로 spanning 할땐 802.1q VLAN. 2byte tag, tag control
- link-layer device
5. link virtualization: MPLS
- Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS)
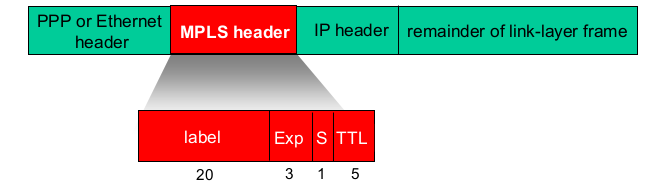
- IP: connectionless, 매 패킷을 독립적으로 전송
- 전파망: connection 위에 전송. 일단 1번 라우팅, 그 다음부턴 그대로 전송
- 첫번째 연결에서 모든 라우팅이나 기타 요구사항으로 리소스 reserve, 이후 그 ID로 모든걸 다 한다.
- label: 20bit짜리. connection 만들어줘서, forwarding을 빨리 할 수 있다.
- routing은 이미 결정 되어 있으므로, ip header가 아닌 MLPS header를 보고 routing
- Virtual circuit (VC) 을 만들어서
- IP header에 주소가 있긴 하다.
- MLPS capable router
- label-switched router
- ip를 뒤져보지 않고, label을 뒤진다.
- MPLS forwading table 존재 (P는 독립적)
- flexibility: IP-목적지로 라우팅
- 얘는 목적지만이 아닌, source 주소, QoS라우팅 가능
- 목적지가 같으면 항상 같은길
- link fail이 났을 때: 좀 더 빨리 복구 가능
- pre-computed packup bath 지정 가능
- MPLS vs IP paths
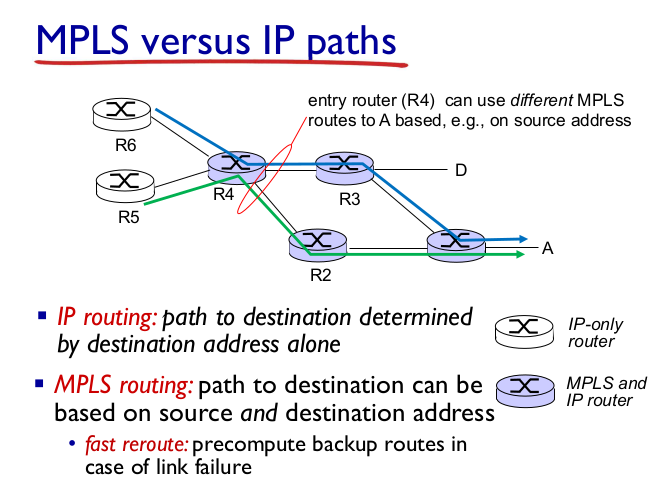
- IP routing: destination 주소로만 forwarding
- MPLS: source를 참고해서 flexible 하게
- fast forwarding 가능
- security에서 유리
- 과금도 유리, label 단위, 시간 재기도 좋다.
- MPLS signaling
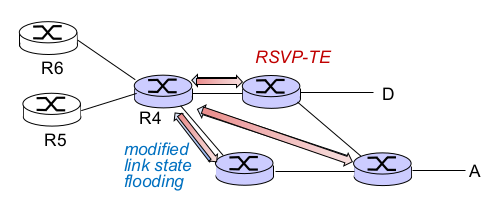
- 사용자 데이터를 보내기 전에 라우팅 정보, 커넥션 만들기, 끊기 등
- control data를 보내는 걸 signaling이라 함
- RSVP
- MPEG => bandwidth 보장 필요. “reservation”
- Reservation Protocol
- connection 만들 때 reservation
- MPLS forwarding tables
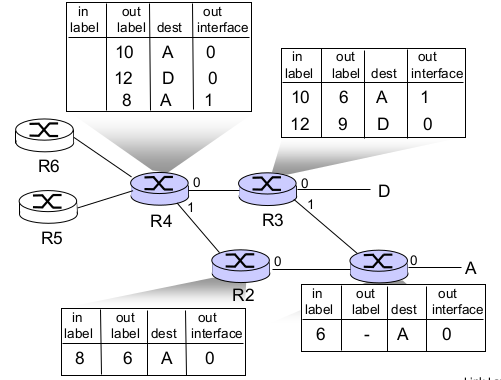
- in label: 들어오는 패킷 label
- out label: 목적지가 A일 때 label을 붙여준다.
- locality: 들어올 때 10, 나갈때 6
- label 중복 가능성이 있으므로
- dest: 목적지
- out interface
- in-label, dest보고 결정.
- data center networking
- 수 만개, 수십만개의 호스트로 구성
- 아마존, 유튜브, Akamai, Google
- challenges
- 각종 application이 있고, 수많은 유저가 있다.
- 어떻게 traffic을 분석해서 가장 효율적으로 access할 수 있을까?
- load balancing: 데이터 센터 트래픽이 상당하므로 bottle neck 발생 가능
- Data center networks
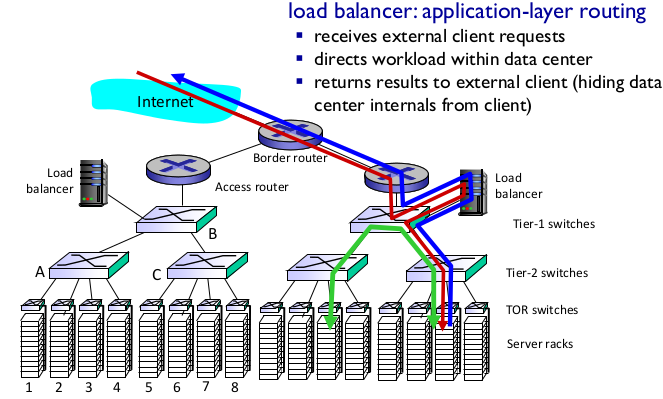
- Tier-1 switch, Tier-2 switch, ToR: Top of the rack 스위치
- load balancer: application-layer routing
- rich interconnection among switches

- switch 간 bottleneck을 해결하기 위해
- 수많은 redundancy를 통해 reliability를 늘린다.
- 이 중 하나가 bottleneck이 걸리면 다른 곳으로 돌아가게. throughput을 늘리자.
- 수 만개, 수십만개의 호스트로 구성